Cytochalasins
Cytochalasans are many types of fungi occurring metabolic products ( metabolites ). In the cells of eukaryotic organisms, they are able to bind to actin filaments . This blocks the polymerisation of this structural protein, which leads to changes in the cell shape (cell morphology ), inhibition of cellular processes such as cell division or even cell death ( apoptosis ).
properties
Cytochalasins have the ability to penetrate cell membranes, prevent cellular translocation, and enucleat cells. Cytochalasins can also influence other aspects of biological processes that are not related to actin polymerization. For example, cytochalasin A and cytochalasin B can also inhibit the transport of monosaccharides across the cell membrane, cytochalasin H regulates plant growth, cytochalasin D inhibits protein synthesis, and cytochalasin E prevents angiogenesis.
It is known that cytochalasins bind to the barbed, rapidly growing plus ends of microfilaments which then block both the assembly and the breakdown of individual actin monomers from the bound end. Once bound, cytochalasins essentially seal the end of the new actin filament. A cytochalasin binds to an actin filament. Studies with cytochalasin D (CD) have shown that the formation of CD actin dimers contains ATP-bound actin. These CD-actin dimers are reduced to CD-actin monomers as a result of ATP hydrolysis. The resulting CD-actin monomer can bind another monomer to reform the CD-actin dimer. CD is very effective; only low concentrations (0.2 μM) are required to prevent membrane disintegration and interrupt treadmilling. The effects of many different cytochalasins on actin filaments were analyzed and higher concentrations (2-20 μM) of CD were needed to remove stress fibers.
In contrast, latrunculin inhibits actin filament polymerization by binding to actin monomers.
use
Actin microfilaments have been extensively studied using cytochalasins. Because of their chemical nature, cytochalasins can help researchers understand the role of actin in various biological processes. The use of cytochalasins has enabled researchers to better understand actin polymerization, cell motility, ripple, cell division, contraction, and cell stiffness. Because of the importance of cytochalasins in understanding the movement of the cytoskeleton and many other biological processes, researchers have created two synthetic cytochalasins.
Cytochalasin has found practical application in thromboelastometry (TEM) whole blood assays for evaluating fibrinogen and fibrin polymerization disorders in the FIBTEM assay on ROTEM. This test is based on the principle that cytochalasin D , the platelet function effectively inhibited by inhibiting the contractile elements very much. Platelet inhibition is more effective than when platelets are blocked by GPIIb / IIIa antagonists . In-vitro and clinical data show that the coagulation strength in FIBTEM increases independently of the platelet count as a function of the fibrinogen concentration. Therefore, fibrinogen deficiency or fibrin polymerization disorders can be detected quickly.
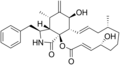
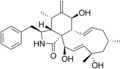
Chemical structures
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b A. M. Haidle and AM Myers: An Enantioselective, Modular, and General Directions to the cytochalasin: Synthesis of L-696.474 and cytochalasin B . In: PNAS . tape 101 , 2004, pp. 12048-12053 , doi : 10.1073 / pnas.0402111101 .
- ↑ a b c d J. A. Cooper: Effects of Cytochalasin and Phalloidin on Actin. In: JCB . tape 105 , 1987, pp. 1473 , doi : 10.1083 / jcb.105.4.1473 .
- ↑ RH Cox et al .: Proton and Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of the Conformation of Cytochalasin H Derivatives and Plant Growth regulating Effects of Cytochalasins . In: J. Agric. Food Chem. Band 31 , 1983, pp. 405-408 , doi : 10.1021 / jf00116a055 .
- ↑ DA Ornelles et al .: Cytochalasin D releases mRNA from the Cytoskeletal Framework and inhibits Protein Synthesis . In: Mol. Cell Biol. Volume 6 , 1986, pp. 1650-1652 , doi : 10.1128 / MCB.6.5.1650 .
- ↑ T. Udagawa et al .: Cytochalasin E, an Epoxide containing Aspergillus-derived fungal Metabolite, inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumor growth . In: J Pharmacol Exp Ther. tape 294 , 2000, pp. 421-427 , PMID 10900214 .
- ↑ DW Goddette and C. Peace: Actin Polymerization. The Mechanism of Action of cytochalasin D . In: J Biol Chem. Volume 261 , 1986, pp. 15974-15980 , PMID 7199055 .
- ↑ a b I. Yahara et al .: Correlation between Effects of 24 different Cytochalasins on cellular Structures and cellular Events and those on Actin in vitro . In: JCB . tape 92 , 1982, pp. 69 , doi : 10.1083 / jcb.92.1.69 .
- ↑ JA May et al .: GPIIb-IIIa Antagonists cause rapid Disaggregation of Platelets pre-treated with Cytochalasin D. Evidence that the Stability of Platelet Aggregates depends on normal Cytoskeletal Assembly . In: Platelets . tape 9 , 1998, pp. 227-232 , doi : 10.1080 / 09537109876744 .
- ↑ T. Lang et al .: Different Effects of Abciximab and Cytochalasin D on Clot Strength in Thrombelastography . In: Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis . tape 2 , 2004, p. 147-153 , doi : 10.1111 / j.1538-7836.2004.00555.x .
- ↑ T. Lang et al .: The Effects of Fibrinogen Levels on Thromboelastometric Variables in the Presence of Thrombocytopenia . In: Anesthesia & Analgesia . tape 108 , 2009, p. 751-758 , doi : 10.1213 / ane.0b013e3181966675 .