Diels-Reese reaction
The Diels-Reese reaction is a name reaction in organic chemistry. It was first described in 1934 by the German chemist Otto Diels (1876–1954) and Johannes Reese. It is a reaction between dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate (or related esters) and hydrazobenzene .
To the reaction
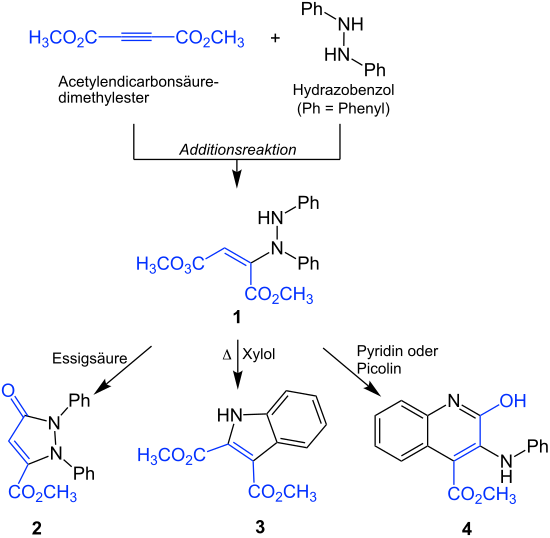
The exact mechanism of the reaction is not known. The proposed mechanism involves an addition reaction between hydrazobenzene and dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate ( blue ). The resulting adduct 1 can be converted into three different heterocyclic compounds under various experimental conditions . This is done by changing the acidic or basic nature of the solvent . With acetic acid as solvent ( acidic ) the reaction gives a diphenylpyrazolone 2 . When heated and with xylene as solvent ( neutral ), the reaction gives an indole 3 . With pyridine or picoline as solvent ( basic ) the reaction results in a carbomethoxyquinoline 4 :
Individual evidence
- ↑ Otto Diels, Johannes Reese: Syntheses in the hydroaromatic series. XX. About the addition of acetylene dicarboxylic acid ester to hydrazobenzene . In: Justus Liebig's Annals of Chemistry . tape 511 , no. 1 , 1934, p. 168 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.19345110114 .
- ^ Zerong Wang: Comprehensive organic name reactions and reagents . John Wiley, Hoboken, NJ 2009, ISBN 978-0-470-63885-9 , pp. 892-895 , doi : 10.1002 / 9780470638859.conrr42 .