Enoxacin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
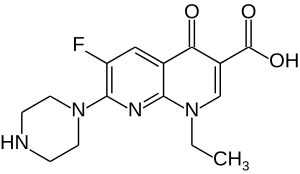
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Enoxacin | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7- (piperazin-1-yl) -1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 17 FN 4 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Gyrase inhibitors |
|||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 320.32 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Enoxacin is a synthetic antibiotic from the second group of fluoroquinolones . Compared to substances from the first group of fluoroquinolones (e.g. norfloxacin ), it has a greater effect and a broader spectrum of activity , which particularly includes gram-negative pathogens. The effect against staphylococci , streptococci including pneumococci , however, is low. Due to the increased interaction potential and lower potency of enoxacin compared to ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin , it has lost its importance in therapy. Enoxacin is bactericidal and has a post-antibiotic effect (see also aminoglycosides ).
spectrum
The spectrum includes many gram-negative pathogens ( Haemophilus and Salmonella species). The effect against staphylococci, streptococci including pneumococci, however, is low.
Side effects
Gastrointestinal complaints such as nausea, stomach pain and diarrhea occur most frequently. Headache, difficulty sleeping, and drowsiness can also occur. All fluoroquinolones have a certain phototoxic potential, which is why direct sunlight should be avoided. Furthermore, tendon ruptures , particularly in the area of the Achilles tendon , have rarely been described, which occurred more frequently due to the simultaneous use of glucocorticoids. The risk of a prolongation of the QT time cannot be ruled out with enoxacin either.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet Enoxacin sesquihydrate, analytical standard from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 7, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Ernst Mutschler, Gerd Geisslinger, Heyo K.Kroemer et al .: Mutschler drug effects , Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart, 2013