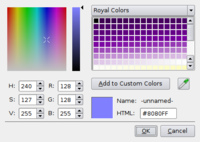
Color picker
A color picker or color mixer is part of the graphical user interface in the software area , with which a color can be selected interactively. The term color picker or color tool is common in the English-speaking world and is also widespread on the German web.

1: gradient field of under 9 selected hue to the color selection
2: color pattern memory locations
3: preview of the selected color
4: Last selected color
5: Pipette
6: hexadecimal color
7: RGB slider
8: HSV slider
9: Selected root
Shapes of color pickers
Color selection dialog
All image editing programs contain color pickers in the form of dialog boxes , for example to select the color of the painting tool .
For this purpose, the user is shown either color palettes with a selection of specified colors or so-called color gradient fields with which brightness and saturation can be precisely determined ("stepless" color selector). When choosing a color, you can often choose between different color spaces . Color pickers often use the HSV color space because it is particularly easy to find the color you want. Sometimes the RGB values are also given in their hexadecimal notation , e.g. B. is used in the HTML source code of websites (see web color ).
- Examples of color selection dialog boxes
A stepless color selection dialog
A GTK + color picker
A Qt color picker
pipette
The eyedropper is a tool that allows you to pick out the color at a specific point in an image. In some desktop programs it is also possible to read out the color number at any position on the screen with the pipette tool. This enables the color to be transferred particularly quickly to other applications. A web designer can read the colors of the customer's logo directly from his website and use them in the design of the website without having to download the graphic and open it in a graphics program. This is usually not possible in an online color picker due to the security restrictions of the browser. Nevertheless, modern web technology now enables the implementation of color selectors that are just as convenient and feature rich as desktop programs and can be executed directly in the browser.
mathematics
The pixel of a typical color monitor consists of a red, green, and blue sub-pixel . The native, that is, the computer's own color space for calculating and displaying the colors is therefore RGB. On a modern computer, the display has a color palette with a color depth of 24 bits . These 24 bits allow 2 24 bit combinations so that 16,777,216 colors can be coded. The native color table is based on the RGB color space , so that a color number can be calculated using the formula of additive color mixing:
, , Thereby, the channels of the RGB color space on the intensity or luminance of the three sub-pixels is set.
1 byte is available for each channel so that the intensity can be specified in 256 levels, ie with numbers from 0 to 255. The basic colors have the numbers for red, for green and for blue. The border colors have the numbers for black and for white, which means that all sub-pixels shine with full power and blend into white in the human eye. Gray tones result when all sub-pixels glow with the same intensity. Medium gray has the number .
The three channels, each with 256 intensity levels, result in 256 ^ 3 possible combinations and thus also 16,777,216 possible combinations:
Modern operating systems use 32 bits for the display. An additional byte is used for the alpha channel , which determines the transparency of the pixel. The alpha channel does not expand the color space, but enables various graphic effects such as realistic shadows under program symbols and windows and anti-aliasing .
The determination of the color in the RGB space is regarded as not intuitive, so that the determination of the color via alternative color spaces is usually offered as support in color selectors. In the HSV color space, for example, the color can be described by hue (hue), saturation (saturation) and lightness value (value). The saturation determines the proximity to gray and brightness the proximity to white or black. The hue is mostly modeled as a circle with the basic colors starting and ending with red at a distance of 120 °: green is 120 °, blue is 240 °. Due to the course from red to green between 0 ° and 120 °, yellow is in the middle at 60 °. Such a gradient gives a clearer arrangement of the color tones than the native RGB table. However, the conversion results in rounding errors, so that an intuitive color space cannot always be clearly mapped to RGB.
Not every monitor can display all colors. There are also monitors that stretch the color space and can therefore display more colors. In this case, a conversion takes place directly in the monitor. The gamut determines the area of the color space that a display or recording device can cover.
attachment
supporting documents
literature
- James D. Foley et al. A. Computer Graphics: Principles and Practice , 2nd Edition, Addison-Wesley 1995, ISBN 0-201-84840-6
Web links
- www.colorpicker.com - online color picker