Fireball (explosion)
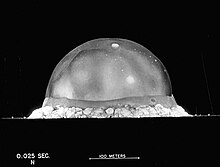
A fireball (also isothermal sphere or fire bubble ) is the general term used for explosions and especially for atomic bomb explosions as the glowing cloud that forms around the center of the explosion. The fireball of a nuclear explosion consists partly of the gaseous remains of the nuclear weapon , but for the most part consists of air that has been heated and partly ionized by radiation or the shock wave . The fireball can be seen as a roughly spherical, brightly glowing cloud and is clearly demarcated from its surroundings, as high-speed recordings of nuclear tests show. Temperatures of more than 1.5 million degrees Celsius can arise in the core of the fireball . If the fireball touches the ground, one speaks of a ground explosion, otherwise of an air explosion.
In non-nuclear explosions, the shape, luminosity, and delineation of the fireball depends on the type of explosive or fuel used . In film productions , pyrotechnic sets mixed with gasoline are often used to create particularly effective, long-lasting fireballs.
Web links
- Fireball of the first atomic bomb explosion as well as a previous TNT test explosion
- Phoenix Simulation (accessed April 6, 2020)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Special Effects (SFX): This is how explosions and shootings are made. HD Austria, accessed on April 30, 2020 .