FISH test
This article was based on formal or substantive deficiencies in the quality assurance biology , see "Genetics and Biochemistry" entered for improvement. This is done in order to bring the quality of the biology articles to an acceptable level. Please help improve this article! Articles that are not significantly improved can be deleted if necessary.
Read the more detailed information in the minimum requirements for biology articles .
Reason: missing sources
The FISH test is a rapid cytogenetic test that is used in particular in the context of prenatal and carcinoma diagnostics . The abbreviation FISH stands for fluorescence in situ hybridization .
FISH test in prenatal diagnosis
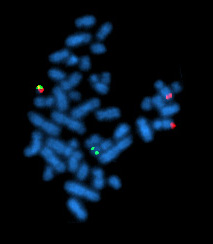
Just a few days after cell removal (e.g. in a chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis ), some chromosome peculiarities can be detected with a high degree of certainty by counting the chromosomes most frequently affected by peculiarities (13, 18, 21, X, Y), provided that suitable cell material is obtained has been.
With the FISH test, numerical changes in the sex chromosomes X and Y can be detected relatively reliably, such as B. Ullrich-Turner syndrome (monosomy X) and triple X syndrome , which only occur in girls, or Klinefelter syndrome , which only occurs in boys and in which the child has an additional X chromosome (XXY instead of XY). A triploidy (triplication of all chromosomes) or tetraploid (quadrupling of all chromosomes) as well as the tripling of individual chromosomes ( trisomy ), as z. B. Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18) or Patau syndrome (trisomy 13) is the case, can be recognized.
For the FISH test, no cells are required in the cell division stage, so that the cells do not have to be cultivated. The result of the examination is usually already available after a day, but is very reduced compared to the detailed chromosome analysis after long-term cultivation: The FISH test can determine whether there are any peculiarities in the number of chromosomes examined in the baby. However, there are also hereditary diseases and disabilities that arise from the fact that certain chromosomes have special features in terms of their structure. The test can only provide limited information here. On the other hand, chromosomes are only checked for structural changes when necessary. For example, Williams-Beuren syndrome , Angelman syndrome, and DiGeorge syndrome can be diagnosed using the FISH test.
It can happen that the cell samples taken from the child are mixed with maternal cells (maternal contamination ), which makes diagnosis difficult and in exceptional cases impossible. This aspect is currently one of the main reasons for diagnostic uncertainties in the FISH test. Trained laboratory staff are, however, able to detect such contamination with a high degree of certainty (e.g. reddish discoloration of the amniotic fluid from the mother's blood). Another factor that can influence the informative value of the result is the number of cells (or cell nuclei) obtained that can be adequately examined. The guideline value recommended by the Professional Association of German Human Geneticists (BVDH) is at least 50.
For the reasons mentioned, the prenatal rapid test cannot replace the detailed analysis of the long-term culture (result after an average of two weeks). Most of the chromosomally-related peculiarities that result from karyotyping according to z. B. amniocentesis are routinely detectable nowadays, cannot be detected by him.
Despite certain diagnostic uncertainties, the test can be helpful if a pregnant woman or a couple of parents does not feel psychologically able to cope with the tension and uncertainty that comes with waiting around two to three weeks for the detailed result of the chromosome examination. A first result can be a little reassuring. The downside must not be forgotten, however, because the FISH test can also produce an undesirable result. In this case, however, the waiting time for the detailed test result could be used to find out about the peculiarities determined by the FISH test. If the diagnosis is finally confirmed, a decision on how to proceed can be made on the basis of the information obtained in advance. Even after a clear eye-catching examination result the FISH test the couple should only the results of other studies (especially the fine ultrasound can) Check to see if they match those of the cell analysis and the FISH test results support before an abortion is considering .
FISH test in cancer diagnosis
As part of carcinoma diagnostics, it is used, for example, as a supplement to the HER2 / neu test for breast cancer to check whether a tumor could react to a corresponding antibody therapy. It is also widely used to define chromosome rearrangements in childhood leukemia.
Web links
- Three images: Positive FISH test for trisomy 21 (A), trisomy 18 (B), trisomy 13 (C) ( Memento from March 11, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
