The form factor is a term used in electrical measurement technology and describes the ratio of effective value to rectified value of a periodic signal . Depending on the shape of the curve, it can assume values from one to infinity.
General For the form factor of a variable, in this case the electrical voltage is selected as the variable , with the period duration:
F.
{\ displaystyle F}
U
{\ displaystyle U}
T
{\ displaystyle T}
F.
=
U
e
f
f
U
G
l
r
=
1
T
∫
t
0
t
0
+
T
u
2
(
τ
)
d
τ
1
T
∫
t
0
t
0
+
T
|
u
(
τ
)
|
d
τ
{\ displaystyle F = {\ frac {U _ {\ mathrm {eff}}} {U _ {\ mathrm {glr}}}} = {\ frac {\ sqrt {{\ frac {1} {T}} \ int _ {t_ {0}} ^ {t_ {0} + T} u ^ {2} (\ tau) d \ tau}} {{\ frac {1} {T}} \ int _ {t_ {0}} ^ {t_ {0} + T} | u (\ tau) | d \ tau}} \}
The form factor is particularly important for the measurement of alternating quantities , but significant because although the effective value to be displayed usually in simpler instruments only rectified value is detected. These devices display 1.11 times the rectified value, which means that they are adjusted to the form factor of a sinusoidal signal
F.
=
1
2
U
^
2
π
U
^
=
π
2
⋅
2
=
π
8th
≈
1,110
7th
.
{\ displaystyle F = {\ frac {{\ frac {1} {\ sqrt {2}}} {\ hat {U}}} {{\ frac {2} {\ pi}} {\ hat {U}} }} = {\ frac {\ pi} {2 \ cdot {\ sqrt {2}}}} = {\ frac {\ pi} {\ sqrt {8}}} \ approx 1 {,} 1107 \.}
In the case of other signal forms (triangle, rectangle, etc.) with other form factors, the measured value is falsified.
In the case of mixed sizes , it makes sense in some situations to specify the form factor for its alternating component rather than for the entire signal.
The ratio of the peak value to the rms value is known as the crest factor or crest factor.
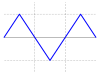
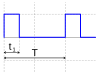
Form factors The following table shows form factors and related quantities for various simple waveforms. They are all independent of the peak value.
Properties of different waveforms
Vibration type
Waveform
Rectification value
Form factor
RMS value
Crest factor
Sine wave
2
π
≈
0.637
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {2} {\ pi}} \ approx 0 {,} 637}
π
2
2
≈
1
,
11
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {\ pi} {2 {\ sqrt {2}}}} \ approx 1 {,} 11}
1
2
≈
0.707
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {1} {\ sqrt {2}}} \ approx 0 {,} 707}
2
≈
1.414
{\ displaystyle {\ sqrt {2}} \ approx 1 {,} 414}
Full oscillation of
2
π
≈
0.637
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {2} {\ pi}} \ approx 0 {,} 637}
π
2
2
≈
1
,
11
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {\ pi} {2 {\ sqrt {2}}}} \ approx 1 {,} 11}
1
2
≈
0.707
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {1} {\ sqrt {2}}} \ approx 0 {,} 707}
2
≈
1.414
{\ displaystyle {\ sqrt {2}} \ approx 1 {,} 414}
Half
1
π
≈
0.318
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {1} {\ pi}} \ approx 0 {,} 318}
π
2
≈
1.571
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {\ pi} {2}} \ approx 1 {,} 571}
1
2
=
0
,
5
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {1} {2}} = 0 {,} 5}
2
{\ displaystyle 2}
Triangular oscillation
1
2
=
0
,
5
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {1} {2}} = 0 {,} 5}
2
3
≈
1.155
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {2} {\ sqrt {3}}} \ approx 1 {,} 155}
1
3
≈
0.577
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {1} {\ sqrt {3}}} \ approx 0 {,} 577}
3
≈
1.732
{\ displaystyle {\ sqrt {3}} \ approx 1 {,} 732}
Sawtooth oscillation
1
2
=
0
,
5
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {1} {2}} = 0 {,} 5}
2
3
≈
1.155
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {2} {\ sqrt {3}}} \ approx 1 {,} 155}
1
3
≈
0.577
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {1} {\ sqrt {3}}} \ approx 0 {,} 577}
3
≈
1.732
{\ displaystyle {\ sqrt {3}} \ approx 1 {,} 732}
Symmetrical
1
{\ displaystyle 1}
1
{\ displaystyle 1}
1
{\ displaystyle 1}
1
{\ displaystyle 1}
PWM signal
t
1
T
{\ displaystyle {\ frac {t_ {1}} {T}}}
T
t
1
{\ displaystyle {\ sqrt {\ frac {T} {t_ {1}}}}}
t
1
T
{\ displaystyle {\ sqrt {\ frac {t_ {1}} {T}}}}
T
t
1
{\ displaystyle {\ sqrt {\ frac {T} {t_ {1}}}}}
Equal size
1
{\ displaystyle 1}
1
{\ displaystyle 1}
1
{\ displaystyle 1}
1
{\ displaystyle 1}
literature R. Patzelt, H. Fürst: Electrical measurement technology . Springer, 1993, ISBN 3-211-82442-1 .
Web links
<img src="https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special:CentralAutoLogin/start?type=1x1" alt="" title="" width="1" height="1" style="border: none; position: absolute;">