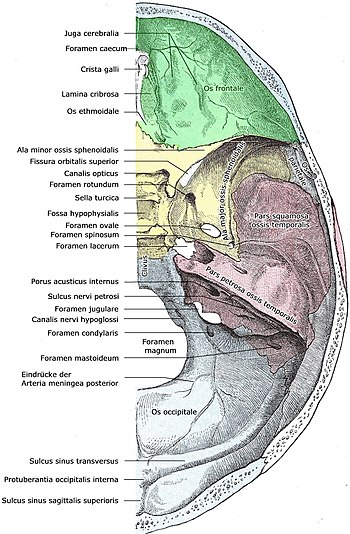
Anterior cranial fossa
The anterior cranial fossa (lat., "Anterior cranial fossa"), in animals fossa rostralis designates a recess in the inner cavity of the skull . It is made up of the central ethmoid bone ( os ethmoidale ) and the temporal and frontal bones placed on the side . The small wing of the sphenoid separates the anterior from the middle cranial fossa ( fossa cranii media ). The anterior cranial fossa contains Juga cerebralia (elevations for cerebral furrows) and Impressiones digitatae("Finger-shaped impressions" of the brain convolutions). In the middle of the pit rises a crest of bone, the crista galli (cockscomb), to which the cerebral sickle ( falx cerebri ), consisting of the hard meninges ( dura mater ), is attached. The foramen caecum is closed in adults.
Skull penetrations
| Entry point | content |
| Lamina cribrosa |
Fila olfactoria of the first cranial nerve
Anterior and posterior ethmoid arteries |
| Foramen caecum | Vena emissaria |