Frontal bone

1st frontal bone (yellow)
2nd parietal bone (parietal bone )
3rd nasal bone (nasal bone )
4th ethmoid bone (ethmoid bone )
5th lacrimal bone (lacrimal bone )
6th sphenoid bone ( sphenoid bone )
7 . occiput (occipital)
8. temporal bone (temporal bone)
9. cheekbone (zygomatic bone)
10. upper jaw (maxilla)
11 lower jaw (mandible)
The paired frontal bone (lat. Os frontale ) is a part of the brain skull . It forms the front roof of the skull and thus the front upper wall of the cranial cavity , and in ruminants a large part of the skull roof. The frontal bones on both sides are connected to each other in the median plane via a cranial suture , the sutura frontalis ("frontal suture ").
description
The frontal bone forms the upper ( margo supraorbitalis ) and rear part of the bony eye socket ( orbit ). The posterior margin is formed by an extension ( processus zygomaticus ossis frontalis ). In carnivores and pigs this process is only short. Here the rear edge of the orbit is only closed by a connective tissue band ( ligamentum orbitale ) that runs between the zygomatic process of the frontal bone and the frontal process of the zygomatic bone .
In humans and other primates , the frontal bone has a distinct bulge above the eyes, which is known as the arch of the eyebrow ( arcus superciliaris ). The glabella lies between the two arches of the eyebrows above the root of the nose .
Between the two bone plates of the frontal bone, a mucous membrane- lined protrusion of the nasal cavity grows . This frontal sinus ( sinus frontalis ) is one of the paranasal sinuses .
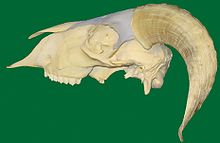
In horn-bearing ruminants , the frontal bone forms a bony horn cone ( processus cornualis ) in the horn . The frontal sinus extends into this process so that the frontal sinus is opened when adult ruminants are dehorned.
See also
literature
- Franz-Viktor Salomon: Bony skeleton . In: Franz-Viktor Salomon et al. (Hrsg.): Anatomie für die Tiermedizin . 3. Edition. Enke, Stuttgart 2015, ISBN 978-3-8304-1288-5 , pp. 96-97 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT) (1998). Terminologia Anatomica . Stuttgart: Thieme