Gassman indole synthesis
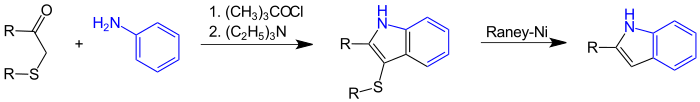
The Gassman indole synthesis is a variant of the Gassman reaction which - starting from aniline or aniline derivatives - leads to substituted indoles . It was first published in 1973 by Paul G. Gassman . With the successive action of tert-butyl hypochlorite and triethylamine, a thioether with a 3-indolyl ring is formed, which can be desulfurized with Raney nickel to the corresponding indole derivative:
A possible reaction mechanism is described in the following scheme:
In a first stage, aniline or mono- N - alkylated anilines are reacted with tert-butyl hypochlorite ( 1 ) to form the corresponding N -chloroaniline ( 3 ), which in turn is reacted with a β-carbonyl sulfide. The intermediate product 4 formed can then be converted into the end product 9 by adding a base , usually triethylamine . The whole synthesis can be carried out as a one-pot reaction without isolation of the intermediate products. The thioether 9 can be easily desulfurized by hydrogenolysis , for example with Raney nickel, to form the 2-substituted indole 10 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Paul G. Gassman, TJ Van Bergen, Gordon. Gruetzmacher: Use of halogen-sulfide complexes in the synthesis of indoles, oxindoles, and alkylated aromatic amines . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 95 , no. September 19 , 1973, p. 6508-6509 , doi : 10.1021 / ja00800a088 .
- ^ Jie Jack Li: Name reactions . Springer, Berlin 2006, ISBN 978-3-540-30030-4 , pp. 257-258 , doi : 10.1007 / 3-540-30031-7_114 .