Glatiramoids
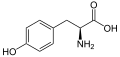
Glatiramoids are heterogeneous mixtures of synthetic polypeptides that consist of the four natural amino acids L - glutamic acid , L - lysine , L - alanine and L - tyrosine ("GLAT"). The proportions of the amino acids are firmly defined, their order in the peptide is random. Glatiramoids are characterized, among other things, by the mean molar mass or mass distribution. They belong to the non-biological complex drugs (NBCDs).
Structural formulas of the amino acids contained in the polypeptide:
Glatiramoids are used or developed for immunomodulatory therapy. So far, the following glatiramoids have been described:
Individual evidence
- ↑ Y. Ramot et al .: Comparative Long-Term Preclinical Safety Evaluation of Two Glatiramoid Compounds (Glatiramer Acetate, Copaxone®, and TV-5010, Protiramer) in Rats and Monkeys. Toxicologic Pathology, 40: 40−54, 2012, doi : 10.1177 / 0192623311424169 .