Golden breasted bearded bird
| Golden breasted bearded bird | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
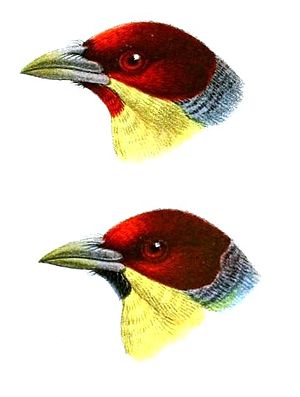
Golden breasted bearded male heads (drawing by John Gerrard Keulemans ). (Above the nominate form E. r. Richardsoni , below the subspecies E. r. Granadensis from southern Colombia and northern Peru, which is often not regarded as independent. These birds are then also assigned to the nominate form.) |
||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||
| Eubucco richardsoni | ||||||||||
| ( GR Gray , 1846) |
The Lemon-throated barbet ( Eubucco richardsoni ) is a bird art from the family of Bart birds . The colorful species, which has a showy sexual dimorphism , is found in South America. Several subspecies are distinguished. The IUCN classifies the golden breasted bearded bird as not endangered ( least concern ).
Appearance
The males of the nominate form reach a wing length of 6.4 to 7.2 centimeters. The tail measures between 4.2 and 5.1 centimeters. The beak length is 1.6 and 1.8 centimeters. Females have similar body dimensions.
The males have some black, forward-pointing bristle-like feathers at the base of their beak. The forehead to the back of the head and the ear covers to the nape are bright red. Birds with slightly more worn plumage show the black base of the feathers. The nape of the neck is pale blue-gray with dark, indistinct horizontal stripes. The rest of the top of the body is green. The control springs are dark green with a bronze shimmer on the upper side, the spring shafts are dark brown. On the underside, the control feathers have a yellowish sheen, the shafts are horn-colored to yellowish horn-colored. In the nominate shape, the chin has a small red or black spot in the middle . The sides of the throat, the rest of the throat and the lower sides of the neck are yellow. The chest and the sides of the chest are red to orange-red. The belly is golden yellow, the sides of the body, the flanks and the belly are striped from olive green to black and green. The beak is short, yellowish to yellow-green. The featherless skin area around the eyes is very narrow. The eyes are red to reddish-maroon. The legs and feet are green, olive green, or gray green.
The females differ very clearly from the males, as they do not show any red on the head. They have a narrow black line around the base of the beak. A black band runs over the eyes along the sides of the neck. There is a white stripe above the eye. A yellow stripe runs over the black band to the end of the neck. The forehead is green and pale gray. The top of the head to the neck is greenish or yellowish. The throat is gray-white. A broad orange stripe runs between the throat and chest. The breast is gray to yellowish gray. The middle of the abdomen is yellow, the sides and flanks are striped green-black.
The golden breasted bearded bird is unmistakable. There is no other bearded bird with an overlapping range that has similar plumage. The scarlet-headed bearded bird is significantly smaller and has a predominantly red skull and a red throat.
Distribution and way of life
The golden-breasted bearded bird has the largest distribution area among the pygmy beards . It stretches from Colombia over the east of Ecuador , the east of Peru to the north of Bolivia . In the east, the distribution area corresponds to the west of the Amazon basin . The golden breasted bearded bird is predominantly a bird of the lowlands. In Colombia and Ecuador it occurs up to 1200 meters, in Peru up to 1000 meters and in Bolivia up to 1100 meters.
The habitat are tropical primary and dense secondary forests . It usually lives solitary, but is occasionally seen in pairs. It usually resides in the middle and upper treetop region. Insects play less of a role in its diet than the Andean bearded bird , but it spends up to 36% of its time searching dry leaves for insects. While foraging he can occasionally be seen in flocks with other bird species. It is usually a little more active than the polka dot whiskers , which has a similar range as the golden breasted whiskers.
The reproductive biology of the golden breasted bearded bird is largely unexplored.
supporting documents
literature
- Lester L. Short, Jennifer FM Horne: Toucans, Barbets and Honeyguides - Ramphastidae, Capitonidae and Indicatoridae . Oxford University Press, Oxford 2001, ISBN 0-19-854666-1
Individual evidence
Web link
- Eubucco richardsoni inthe IUCN 2013 Red List of Threatened Species . Listed by: BirdLife International, 2012. Retrieved February 2, 2014.