Hammerschmiede (Talhausen)
The Hammerschmiede an der Glems was a hydropower-operated factory in the district of the Markgröningen district of Talhausen .
history
Blacksmith shop
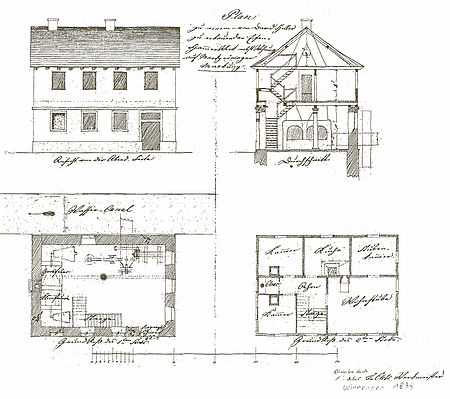
The construction of the hammer forge was requested in 1838 by master blacksmith David Heller from Leutenbach for a location to the left of the Glems and in 1840 it was finally built on the right of the Glems instead of a farm at the foot of the Schlüsselberg. The building measured 8.6 by 5.7 meters, lay on an 80 meter long canal branched off to the right of the Glems and was first propelled by one, later by two undershot water wheels. On the northern front of the forge, two meals were set up for large and small fires, each with a bellows in the corners. Plowshares, shovels, spades, pickaxes, hoes and karsts, hatchets and axes, hammers and chisels as well as iron tires for barrels and wheels were made. Or special one-offs such as shafts and bearings to order from the other millers in the valley.
Second mainstay
In 1860, Heller received permission from the Oberamt and the city to install an undershot water wheel to operate a grinding mill with hemp grater next to the hammer forge.
Factory operation
Around 1880 Johann F. Keuerleber set up a machine parts and tool factory here. In 1908 it received a 5 m high and 1.21 m wide medium-sized cellular wheel, which delivered an output of 5.4 hp at a water flow rate of 300 l / s. In 1920 the water level and gradient were increased by 34 cm and the water wheel was replaced by a Francis turbine, which now supplied electricity to operate the machines in the expanded factory. During the Second World War, the factory and its workforce were classified as "vital to the war effort". After that, the factory produced drilling machines. They were driven by handcart to the train station in Markgröningen, from where they were driven to Holland. Cart spindles for handcarts and metal loops for telegraph poles were also manufactured here.
Relics
In 1958 Robert Keuerleber gave up the production facility and relocated the factory to Markgröningen . In 1975, Keuerleber renounced the water rights to the Glems. The Mühlkanal was then filled and the weir was removed. The building of the former hammer forge, built in 1839/40, and the Keuerlebersche factory building are still there.
literature
- Hermann Beck: The hammer forge near Talhausen . In: Müller, Mühlen, Wasserkraft . Volume 5 of the series "Through the city glasses, history and stories about Markgröningen", ed. v. Working group on historical research, heritage and monument preservation in Markgröningen. Markgröningen 1995. pp. 162-172.
- Frieder Schmidt: The Gröningen hammer mill as a technical monument . Stuttgart: Theiss, 1984.
- Thomas Schulz: Mill Atlas Baden-Württemberg , Vol. 3, The mills in the Ludwigsburg district . Remshalden-Buoch: Manfred Hennecke, 1999, ISBN 3-927981-63-X .
- Information board on Glemsmühlenweg
Individual evidence
- ↑ Bundle of files from drive 21 (later T 48) in the archive of the Ludwigsburg Oberamt at the Ludwigsburg district office.
- ^ Hermann Beck: The hammer forge at Talhausen . In: Müller, Mühlen, Wasserkraft . Volume 5 of the series "Through the city glasses, history and stories about Markgröningen", ed. v. Working group on historical research, heritage and monument preservation in Markgröningen. Markgröningen 1995. p. 162ff.
- ^ Hermann Beck: The hammer forge at Talhausen . In: Müller, Mühlen, Wasserkraft . Volume 5 of the series "Through the city glasses, history and stories about Markgröningen", ed. v. Working group on historical research, heritage and monument preservation in Markgröningen. Markgröningen 1995. p. 167ff.
- ^ Hermann Beck: The hammer forge at Talhausen . In: Müller, Mühlen, Wasserkraft . Volume 5 of the series "Through the city glasses, history and stories about Markgröningen", ed. v. Working group on historical research, heritage and monument preservation in Markgröningen. Markgröningen 1995. pp. 170-172.
See also
Web links
- Map and information about the Glemsmühlenweg
- List of cultural monuments in Markgröningen (2011) (PDF; 33 kB)
Coordinates: 48 ° 54 '53.6 " N , 9 ° 3' 55.2" E