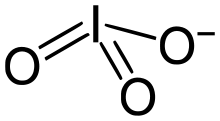
Iodates
Iodates are salts of iodic acid with the anion IO 3 - . All iodates are strong oxidizing agents . They are more stable and at the same time significantly weaker in their oxidizing effect than bromates and chlorates . In mixture with combustible substances iodates are sensitive to impact and easily lead to explosions.
In nature Iodates come in ocean water and in Chilean nitrate and Tang - and algae ashes before. Chile nitrate contains up to 0.1% iodate. Today they are the most important technical basis for iodine production.
“Iodized table salt ” contains sodium and potassium iodate for goiter prophylaxis . Iodates give with sulfite as a reducing agent , the Landolt-time response . Here, the deep blue iodine creates strength - complex after a concentration-dependent reaction time.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Brockhaus ABC Chemie , VEB FA Brockhaus Verlag Leipzig 1965, p. 604.
- ^ The distribution of iodide at the sea surface. Rosie Chance, Alex R Baker, Lucy Carpenter, Tim D Jickells; In: Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts 06/2014; doi : 10.1039 / c4em00139g
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 3: H-L. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1983, ISBN 3-440-04513-7 , p. 2315.