Mixture of isomers
In organic chemistry, an isomer mixture is a mixture of substances composed of two or more isomers . These isomers can be constitutional or stereoisomers ( mixture of stereoisomers ). Mixtures of isomers of different constitutional isomers exist in cracking gases, for example, where isomers of different short-chain hydrocarbons are present as a mixture of isomers.
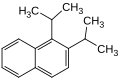
Example: DIPN isomer mixture
Mixtures of isomers can often be found in technical products; an example of this is the DIPN isomer mixture , which contains numerous isomers of diisopropylnaphthalenes. Such technically important isomer mixtures often have their own CAS number as a mixture , although their individual components may already be registered under other CAS numbers.
- Different isomers of diisopropylnaphthalene
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on isomerism. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed December 7, 2018.
- ↑ Guido Kickelbick: Chemistry for Engineers . Pearson Deutschland GmbH, 2008, ISBN 978-3-8273-7267-3 , p. 332 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Studies on diisopropylnaphthalene substitutional isomerism . In: Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical . tape 170 , no. 1-2 , May 14, 2001, ISSN 1381-1169 , pp. 95-99 , doi : 10.1016 / S1381-1169 (00) 00427-1 .
- ↑ Entry on CAS Registry Number. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 7, 2018.
- ^ Common Chemistry - Search Chemical Names and CAS Registry Numbers. Retrieved December 7, 2018 .