Caroline fruit pigeon
| Caroline fruit pigeon | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Caroline fruit pigeon, illustration from 1832 |
||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||
| Ducula oceanica | ||||||||||
| ( Desmarest , 1826) |
The Caroline fruit pigeon ( Ducula oceanica ) is a large species of pigeon birds that is one of the fruit pigeons . It occurs in several subspecies exclusively in Micronesia in the western Pacific.
The population of the Peales fruit pigeon was classified in the IUCN's Red List of Threatened Species in 2016 as “ Near Threatened (NT) ” = “potentially endangered”.
Appearance
The Karolinen fruit pigeon reaches a body length of about 36 centimeters. The tail accounts for 14.2 to 14.5 centimeters. The beak is 2.2 to 2.4 centimeters long. There is no noticeable gender dimorphism . The females are just a little darker in color.
The black wax skin is enlarged and forms a hump. The feathers at the base of the beak are whitish and then turn into an ash gray on the front of the head, on the reins, the crown and the neck. The coat is dark green. The elytra are the same color. The hand and arm wings are blackish and shimmer greenish on the outside flags. The back and the upper tail-coverts are dark green, the tail feathers are blackish.
The chin is whitish, the throat, the ear covers, the neck and the chest are light gray. The belly, the thighs, the rump and the under tail-coverts are dark wine-brown. The beak is slate gray. The feet are bright red.
Fledglings are similar to adult birds. However, their back and rump are not yet as pronounced green.
Distribution area
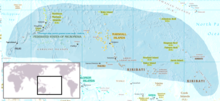
The Caroline fruit pigeon is a type of Micronesia. It occurs here on the Palau Islands , Yap , Chuuk , Pohnpei and originally also on Kiribati . However, the IUCN thinks it is likely that the Caroline fruit pigeon is now extinct on Kiribati. The pigeon is exposed to considerable hunting pressure in its area of distribution. It is generally more common in regions that are far from human settlement.
On the islands, the carolline pigeon generally inhabits the forests of the island's interior. It can also be found on coconut plantations in low atolls.
Way of life
The Caroline fruit pigeon is usually solitary. It is extremely shy wherever it is hunted. Their food spectrum includes fruits, berries and large seeds up to a diameter of 2.3 centimeters. It finds its food in the treetops, where it climbs and picks the fruit directly from the branches. Often it even hangs upside down from the branches.
literature
- David Gibbs, Eustace Barnes and John Cox: Pigeons and Doves - A Guide to the Pigeons and Doves of the World . Pica Press, Sussex 2001, ISBN 90-74345-26-3 .
- Gerhard Rösler: The wild pigeons of the earth - free living, keeping and breeding . M. & H. Schaper Verlag, Alfeld-Hannover 1996, ISBN 3-7944-0184-0 .
- Edward Clive Dickinson, Murray D. Bruce, Normand David: A review of the authorship and dates of publication of birds newly described from the ʺ Voyage de la Coquille ʺ (1822‐1825) with comments on some spellings . In: Zoological Bibliography . tape 3 , no. 5 , 2015, p. 69-162 ( avespress.com [PDF]).
Web links
- Ducula oceanica in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2015 Posted by: BirdLife International, 2015. Accessed December 3, 2016th