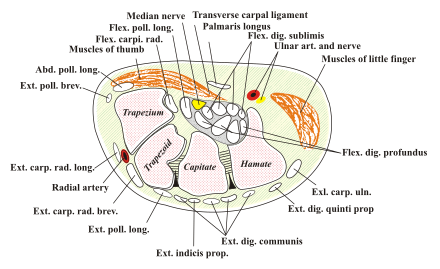
Carpal tunnel
The carpal tunnel ( Canalis carpi ) is a nerve-muscle passage on the palm-side (palmar) side of the forearm at the level of the wrist ( articulatio radiocarpalis ). It represents a tunnel formed by bone and connective tissue in an anatomical groove between the carpal bones . Its posterior wall is formed by the carpal bones and the ligamentum carpi radiatum , in front it is closed by the anterior portion of the retinaculum flexorum . The nine tendons of the finger flexors and the median nerve pass through the carpal tunnel . On the thumb side of the carpal tunnel, the tendon of the radial hand flexor runs in its own tendon sheath , which is separated from the carpal tunnel by connective tissue. Some authors include the flexor carpi radialis muscle as part of the carpal tunnel.
A narrowing of the carpal tunnel with pressure on the median arm nerves is known as carpal tunnel syndrome .
literature
- Michel Merle: Surgery of the hand: rheumatism, osteoarthritis, nerve congestion . Georg Thieme, Stuttgart 2009, ISBN 978-3-13-148151-1 , p. 391 .