Knorr pyrrole synthesis
The Knorr pyrrole synthesis is a common chemical reaction for the synthesis of substituted pyrroles . It is named after its discoverer, the German chemist Ludwig Knorr , and is one of the name reactions . In this reaction, α-amino-ketones and β-ketoesters are converted into pyrroles. The reaction is carried out in the presence of zinc and takes place at room temperature due to the high reactivity of the α-amino-ketones. Since α-aminoketones are not stable and enter into a condensation reaction with themselves , they have to be released in situ , for example from the oximes . The heterocycles obtained are also referred to as Knorr-Pyrroles .
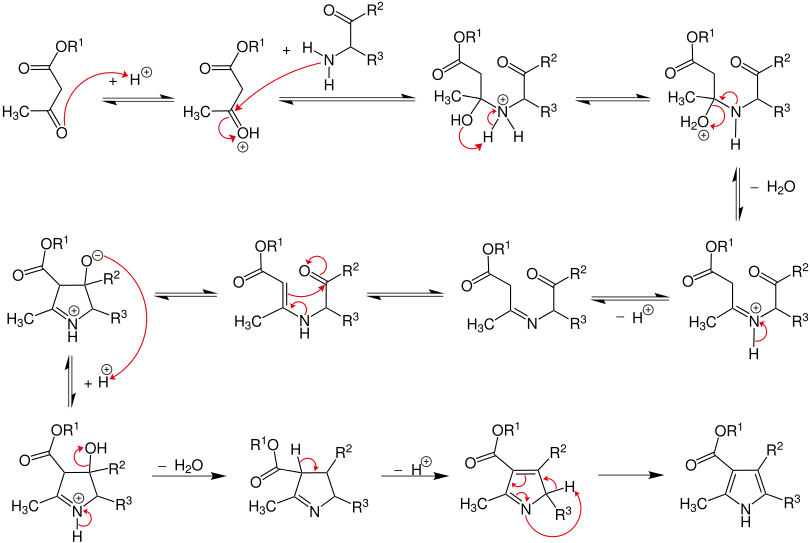
Reaction mechanism
In the first step, the β-ketoester is protonated and then attacked by the α-aminoketone. After intramolecular proton transfer from ammonium to the hydroxy group and elimination of water, the imine is formed after subsequent deprotonation. This tautomerizes to an enamine . By attack of the double bond on the electron-poor carbonyl carbon, an N-heterocycle is now formed. In the next step, the negatively charged oxygen atom is protonated by the formation of an imine to the hydroxyl group, which finally forms the pyrrole after the final elimination of water and formation of a further double bond with renewed imine / enamine tautomerism .
In the original Knorr-Pyrrole synthesis, two equivalents of ethyl acetoacetate were converted. One equivalent was converted into the 2-oximinoacetoacetic acid ester using glacial acetic acid and sodium nitrite . Zinc dust now reduces the oxime to the active amine and the condensation reaction can start.
There are numerous more modern variants of the classic Knorr process. Levi and Zanetti have developed an extension of the Knorr pyrrole synthesis to include acetylacetone (2,4-pentanedione), which is reacted with the oxime to form pyrroles.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Knorr, L. Reports of the German Chemical Society , 1884 , 17 , 1635.
- ↑ Knorr, L. Liebigs Ann. Chem. , 1886 , 236 , 290.
- ↑ Knorr, L .; Lange, H. Reports of the German Chemical Society , 1902 , 35 , 2998.
- ^ Corwin, AH Heterocyclic Compounds , 1950 , 1 , 287.
- ↑ Fischer, H .: 2,4-Dimethyl-3,5-Dicarbethoxypyrrole In: Organic Syntheses . 15, 1935, p. 17, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.015.0017 ; Coll. Vol. 2, 1943, p. 202 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Fischer, H .: Kryptopyrrole In: Organic Syntheses . 21, 1941, p. 67, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.021.0067 ; Coll. Vol. 3, 1955, p. 513 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Zanetti, CU; Levi, E. Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1894, 24, I, 546.