Radiation protection area
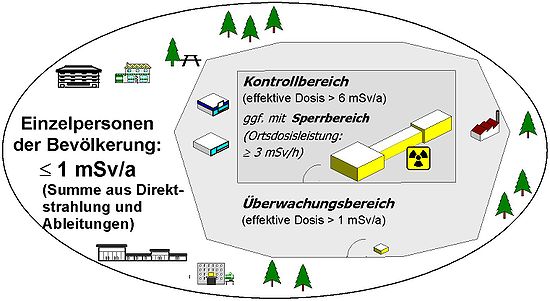
In Germany, a radiation protection area is a spatially separated area in which people can be exposed to ionizing radiation that is above the limit value for the general national territory. Radiation protection areas must be in accordance with national ( Radiation Protection Ordinance ) and EU law for nuclear facilities (e.g. nuclear power plants or fuel element factories ), for interim, intermediate or final storage of radioactive waste , for plants for the generation of ionizing radiation (e.g. particle accelerators ), but also for a simple X-ray system as well as when handling artificially generated radioactive substances (e.g. laboratory, nuclear medicine therapy / diagnosis ). A distinction is made between three radiation protection areas:
- Monitoring area
- Control area
- Restricted area
The purpose of these three radiation protection areas is to protect the population and, in particular, the operating personnel from the effects of ionizing radiation. They are highlighted by structural measures and clear labeling (e.g. "control area"). The limits of the three radiation protection areas are defined by the dose that a person can receive within the respective area through external or internal radiation exposure . Since these are operational protection areas, a length of stay of 40 hours per week and 50 weeks per year (i.e. 2000 hours per year) can be assumed, unless there is any other justified information about the length of stay.
It should be noted that the values are possible loads in this area, not actual values. This means that even within radiation protection areas (especially in the monitored area) there is usually no actually increased radiation exposure. It should also be noted that only radiation from non-natural sources is taken into account. The natural radiation exposure in Germany averages 2.4 mSv per year, which is a multiple of the limit value for monitoring areas.
The three areas are defined in Germany in accordance with Section 52 (2) of the Radiation Protection Ordinance.
Access to radiation protection areas is not free. Section 55 of the Radiation Protection Ordinance specifies when access to a surveillance, control and restricted area is permitted.
For all other areas of a company that are not radiation protection areas, the limit value for the general national territory for the local dose rate of 1 mSv per year applies.
Monitoring area
Monitoring areas are the areas in which people can receive an effective dose higher than 1 mSv or organ doses higher than 15 mSv for the lens of the eye or 50 mSv for the skin, hands, forearms, feet and ankles in a calendar year. Often the entire company site is viewed as a surveillance area and (for example in the case of nuclear power plants) separated from the general national territory by a fence or similar measures.
Control area
The control area is usually enclosed by the monitoring area. In it, people can receive an effective dose of 6 mSv per calendar year or organ doses higher than 45 mSv per calendar year for the eye lens or 150 mSv per calendar year for the skin, hands, forearms, feet and ankles. Control areas must be delimited and clearly marked. A controlled area may only be entered to carry out or maintain the intended operational processes. Visitors only have access with official permission. For people who are in the controlled area, the body doses must be determined - usually with an official dosimeter . Before the initial access and then at least once a year, instruction must be given, in particular about the radiation protection measures to be used.
Restricted area
Restricted areas are areas within a controlled area in which the local dose rate can be higher than 3 mSv per hour. People may only be allowed to stay in a restricted area if they have to work under the supervision of a commissioned, competent person to carry out the intended operational processes or for compelling reasons. Restricted areas are to be demarcated and clearly marked.
swell
- ↑ Glossary Radiation Protection from Forschungszentrum Jülich with a sketch of the radiation protection areas and further explanations
Web links
- Page no longer available , search in web archives: Federal Office for Radiation Protection Switzerland
- The "Radiation Protection Glossary" from Forschungszentrum Jülich (safety and radiation protection) with a focus on operational radiation protection and the basics of radiation protection.
- The Radiation Protection Glossary of the Federal Office for Radiation Protection (BfS) ( Memento dated May 2, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) contains terms from various scientific disciplines and from nuclear technology, including final disposal and abbreviations.