Conductor connection
In electrical power engineering, a conductor short-circuit is a faulty connection or bridging between different electrical conductors if the electrical consumer with its load resistance or parts of the load resistance is in the fault circuit . If there is no part of the load resistance in the fault circuit, the conductor short- circuit becomes an electrical short circuit .
The difference to a short circuit is that in the event of a short circuit, the short circuit current (fault current in the event of a short circuit) is only limited by the generally lowest possible network impedance . In the event of a conductor short-circuit, the fault current is also limited by the load resistance in the fault current circuit, which is usually significantly higher than the network impedance, which means that the fault currents in the event of a conductor short-circuit are generally significantly lower than in the event of a short circuit. A conductor short-circuit may not trigger overcurrent protection devices such as fuses or circuit breakers . Possible dangers of conductor shortages are electrical accidents and indirect dangers such as fires caused by arcing faults or a risk of injury to machines or systems that unintentionally continue to run or start when a conductor is shorted. A conductor short-circuit can be caused by defective insulation .
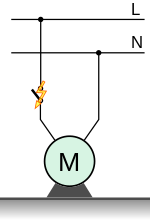
An example of a conductor short-circuit is a defective switch, as shown in the adjacent figure, which is bridged by an insulation fault when it is switched off and can cause the electric motor M to start or continue to run .
swell
- Electric current hazards. Protective measures and protective devices. (PDF; 10.3 MB) University of Duisburg-Essen (lecture slides), accessed on March 28, 2013 .
- Stefan Schmid Gaiser: Wire connection. Retrieved March 28, 2013 .