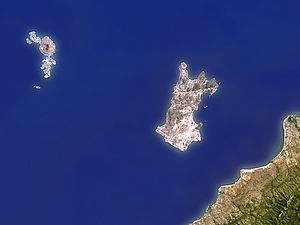
Likoma (island)
| Likoma | ||
|---|---|---|
| Islands Chizumulu (l.) And Likoma (r.) | ||
| Waters | Lake Malawi | |
| Geographical location | 12 ° 4 ′ 0 ″ S , 34 ° 44 ′ 0 ″ E | |
|
|
||
| length | 7.7 km | |
| width | 4 km | |
| surface | 15 km² | |
| Highest elevation | Phonombo and Njakwa Peak 605 m |
|
| Residents | 10,440 696 inhabitants / km² |
|
| main place | Chipyela | |
Likoma , also known as the Isle of Baobab , is a small island in Lake Malawi . It belongs to Malawi , but is located as an enclave with its neighboring island Chizumulu in the territorial waters of Mozambique .
geography
Likoma is administratively part of the Likoma district , with the same name as the island and is part of the Northern Region . The island is only 5 km from mainland Mozambique. It is 10 km to the neighboring island of Chizumulu and the mainland of Malawi can be reached in 56 km. A crossing to the nearest port in Malawi, to Nkhata Bay, takes about 5 hours on the almost 40 nautical miles long route. Likoma is a good 2 km wide at its narrowest point and measures almost 8 km in length. The approximately 15 km² large island extends in a north-easterly direction along the shoreline to Mozambique. There are two equally high elevations on the island , Phonombo and Njakwa Peak . Both bring it to a height of 605 m. The otherwise rocky coastline of the island has numerous bays with sandy beaches all around.
population
Likoma currently has a little more than 7,000 inhabitants (2009) , who are spread over around a dozen villages.
The ethnic group consists of 75% Nyanja , 10% Chewa and 10% Tonga . The remaining 5% are from other ethnic groups. The Tonga are mainly found in two villages in the southern part of the island, while the other tribes have mostly settled around the island's trading centers.
Nyanja is usually used as the language . Other dialects such as Cobue and Tonga occur more frequently on the neighboring island of Chizumulu. 99% of the population are Christians and mainly belong to the Anglican Church , which opened its first mission on the island in 1903.
Agriculture and food supply
Part of the population lives from agriculture and supplies the island with cassava and corn . Another part lives from fishing. Some of the fish is sold to Mozambique or Malawi. Baobabs and mangoes cover another part of the food supply.
However, since the number of families who do not grow their own food is higher on Likoma than in the rest of the country, the population cannot provide for themselves and needs food from Malawi and Mozambique. When food prices rise, it creates supply problems on the island.
nature and landscape
The island was originally entirely forested, but the need for human habitat has taken a toll on the forest over the years. The northeastern tip of the island still has remains of this original forest. This forest, known as the Makungwa Village Forest Area , has now been placed under protection and the Cluny Wildlife Trust , an NGO , has set itself the goal of preserving this natural habitat. In 2007/2008, in the rainy season, 16,000 seedlings were planted for this .
Infrastructure
The island can only be reached by sea or by air. The old-looking steamer Ilala from Malawi Lake Services comes by twice a week , supplying the island with everything it needs and transporting passengers and vehicles to and from Malawi and Tanzania . The island has a small network of unpaved roads, with the main road running across the island from north to south. Ulendo Airlink connects the island to the mainland via the airstrip . For the connection to Mozambique, locals provide their daily services with their small boats. From Ulisa in the west of the island there are boats to the neighboring island of Chizumulu.
economy
Economically, Likoma has nothing to offer except tourism. There are a few lodges for backpackers and for holidaymakers with demands on average standards. The district administration and the Malawian government are trying to develop the two islands for tourism.
The Ministry of Tourism, Wildlife and Culture estimates the potential of visitors to Malawi at around half a million per year in the next few years. From this potential, the tourists for the two islands could consist of 40% locals, 35% from South Africa , Mozambique and Tanzania and 25% from the rest of the world.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Logical Framework, Schedule of Activities, Budget and Institutional Framework of the Likoma Pilot Social Cash Transfer Scheme , Department of Poverty and Disaster Management Affairs, Ministry of Women and Child Development, the Likoma District Assembly and UNICEF , 12.-14. May 2007.
- ↑ Stéphane Helleringer, among others, The Likoma Network Study: Context, data collection, and initial results , in: Demographic Research, Volume 21, Article 15, p. 427–468, Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research, Rostock, October 9, 2009.
- ^ District Education Plan (DEP) 2008 / 09–2001 / 11 , Likoma District Assembly, Likoma, December 2007.
- ^ Post-Harvest Food Security and Maize Marketing Monitoring Trip Report , FEWS-NET, Lilongwe, June 2008.
- ↑ Likoma, Island Sites , Malawi Investment Promotion Agency, Ministry of Tourism, Wildlife and Culture, Lolongwe, June 2007.