Left bundle branch block
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| I44.7 | Left bundle branch block, unspecified |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
A left bundle branch block ( LSB ) is a disorder of the conduction system of the heart . A line delay in the left Tawara leg is characteristic of the disturbance . The diagnosis is made by means of an EKG .
definition
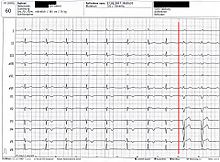
Left bundle branch block is defined as an extension of the interval from the beginning of the QRS complex to the point of final negativity (GNB, greatest negativity, also known as the upper transition point (OUP)) in the left chest wall leads V 5 or V 6 to at least 0.06 Seconds. The QRS width then further defines the difference between an incomplete left bundle branch block with a QRS complex of up to 0.12 seconds and a complete left bundle branch block with a QRS duration of over 0.12 seconds. Another diagnostic criterion for a complete left bundle branch block are notched or indistinct R-waves in I, avL, V5, V6.
Pathophysiology
Hemodynamically , the left bundle branch block leads to a pendulum phenomenon of the left ventricle during contraction . A complete left bundle branch block is a pathological (disease-related) finding. Coronary artery disease , arterial hypertension or cardiomyopathy are often the cause .
interpretation
In contrast to the right bundle branch block, the left bundle branch block is to be regarded as more serious, since the left ventricle does the main part of the pumping work of the heart.
If the left bundle branch block is present , the ECG can no longer be used reliably for heart attack diagnosis, since a repolarization disorder occurs consecutively . The ST segment is heavily modified, which means that it is not easy to interpret in the sense of an ischemic indication . The Sgarbossa criteria can be used to estimate the probability of acute myocardial ischemia. With a normal ECG preliminary examination, a freshly occurring LSB can indicate an acute coronary heart disease (myocardial ischemia), e.g. B. an acute heart attack. Together with the corresponding clinical symptoms ( chest pain , shortness of breath ) or with an increase in heart-specific laboratory markers ( troponin , creatine kinase ), there is an indication for prompt invasive diagnostics in the context of a cardiac catheter examination .
to form
A distinction is made between the following forms:
- Left bundle branch block
- Left anterior hemiblock
- Left posterior hemiblock
Individual evidence
- ^ Galen S. Wagner, Peter Macfarlane, Hein Wellens, Mark Josephson, Anton Gorgels et al .: AHA / ACCF / HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram: Part VI: Acute Ischemia / Infarction A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society Endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Volume 53, Issue 11, 17 March 2009, Pages 1003-1011, doi: 10.1016 / j.jacc.2008.12.016
- ^ STEMI in left bundle branch block - Sgarbossa criteria. In: foamina.blog. May 25, 2015, accessed February 25, 2019 .


