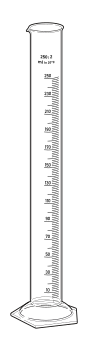Graduated cylinder
- Measuring cylinder 250 ml, with "In" marking
A measuring cylinder is a vertical, hollow cylinder with a spout and a stand, which is provided with a scale ( length ) to measure volumes . Measuring cylinders are also used to determine bulk density . They are available in high or low form. The associated standard is DIN EN ISO 4788 Laboratory glassware - measuring cylinders and mixing cylinders .
In the laboratory , measuring cylinders made of glass are mostly used; but they can also consist of plastic . There are also measuring cylinders which, with the exception of the plastic base, are made of glass.
Standing cylinders have the same shape as measuring cylinders, but no scale.
The point at which a measuring cylinder is read has a curved surface ( meniscus ) due to the hydrophilic interaction of the water with glass . The scale of the measuring cylinder only shows the correct volume if the lowest point of the meniscus is free from parallax on the upper edge of the scale mark. When reading, the eye should always be at the level of the scale mark to be read. An imprint "In" indicates that the measuring cylinder has been "adjusted for sprue". This means that the measured volume is in the vessel, the amount of liquid taken up corresponds to the volume information printed on it. When emptying into another container, a residual amount always sticks to the wall of the measuring cylinder. Measuring cylinders are often used incorrectly as "Ex" volumetric instruments, although they have not been "adjusted to the process".
Mixing cylinder
A mixing cylinder is a measuring cylinder that has a standard joint (NS) instead of a spout, is closed with a joint stopper and can thus be used to mix measured liquids.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Brockhaus ABC Chemie , VEB FA Brockhaus Verlag Leipzig 1965, p. 864.