Micro projector
A microprojector is a device with which transparent microscopic specimens are projected with light onto a screen. This enables multiple viewers to view the microscope slide at the same time.
Projection microscope
With a projection microscope , the specimen is projected onto a transparent screen , which forms a unit with the microscope. If the image is viewed from a normal distance of approx. 25 cm, all details can be seen in the projected image that are also recognizable when viewed directly through a microscope of the same magnification. The device can expediently be used for determining the amount of particles or for determining their size.
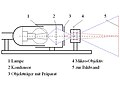
Lighting with a simple condenser
For a limited magnification (approx. 250 ×), illumination based on the principle of the slide projector ( interwoven beam path ) is sufficient . A condenser images the light field of the lamp in the micro lens. The specimen is projected onto a screen by the micro lens. A simple solution for overview preparations can be a microscope attachment for a slide projector. The objective of the slide projector is exchanged for the microscope attachment. Here, too, the light field of the lamp is imaged via additional condenser lenses in the micro-objective.
Lighting according to "Koehler"
If the micro-projection with strong micro-lenses is to reproduce fine details with the highest possible illuminance, lighting according to the Koehler method must be provided. The mode of operation consists of several nested mapping processes. The image of the light source is optimally reproduced in the lens. Appropriate iris diaphragms only illuminate the part of the specimen that is to be projected, the other parts are shaded to protect them. The micro lens is also supplemented by the eyepiece, with which the intermediate image is projected from the lens onto the screen.
Projection with an intermediate slide or with a video projector
As an alternative to direct microprojection, it is also possible to use an "intermediate slide". This slide can be projected with a slide projector and the conditions for a good projection can be better maintained. The same conditions also apply to the electronic transmission and processing of data from the microscope for projection with a video projector .
Comment on viewing conditions
Special viewing conditions must be met for microprojection. Due to the limited resolution and recognizability of small details, the viewing distance of the projected image must be reduced. It will expediently be limited to 2 to 3 times the screen width. Another aspect is the low image brightness. The illuminance of the projected image on the screen should be 5 times higher than the illuminance of the room light, so the room should be darkened considerably.
Individual evidence
- ^ Hermann Beyer: Handbuch der Mikoskopie , VEB Verlag Technik Berlin 1977, page 389.
- ^ F. Paul Liesegang: The projection system . in: Scientific applications of photography first part. Published by Julius Springer, Vienna 1931, page 268.
- ^ F. Paul Liesegang: Introduction to the nature and mode of operation of the still projector . Verlag, Ed Liesegang Düsseldorf, 1936, page 53.
- ^ F. Paul Liesegang: Introduction to the nature and mode of operation of the still projector . Publisher, Ed. Liesegang Düsseldorf, 1936, page 56.
- ^ Hermann Beyer: Handbuch der Mikoskopie, VEB Verlag Technik Berlin 1977, page 391.
- ^ Hermann Beyer: Handbook of microscopy . VEB Verlag Technik Berlin 1977, page 390.