Mongozmaki
| Mongozmaki | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Mongozmaki ( Eulemur mongoz ), male |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Eulemur Mongoz | ||||||||||||
| ( Linnaeus , 1766) |
The Mongozmaki ( Eulemur mongoz ) is a species of primate from the family of ordinary Makis (Lemuridae) within the lemurs (Lemuriformes).
features
Mongozmakis reach a head body length of 30 to 35 centimeters, the long, bushy tail measures 45 to 48 centimeters. Their weight is 1.1 to 1.6 kilograms and are among the smallest representatives of the common Makis. The two sexes differ in their coloration: the fur of the males is gray-brown on top, the belly is light gray, the cheeks, throat and neck are strikingly reddish. The females are a bit lighter than the males, their fur is gray on the back and light gray to beige on the belly, the face is blackish gray, the cheeks and throat are whitish. The elongated snout is light gray in both sexes, the eyes orange.
distribution and habitat
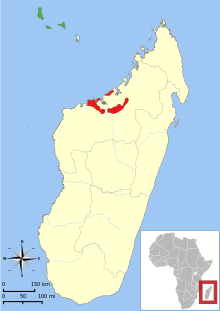
Mongozmakis live in a small area in northwestern Madagascar , and they were also introduced on the Comoros islands of Anjouan , Mohéli and Grande Comore . Their habitat are dry, deciduous forests. In the Comoros, however, they live in moist forests.
Lifestyle and diet
Mongozmakis do not have fixed times of activity, they are cathemeral (active both day and night). In the rainy season they are more active during the day, in the dry season they are more active at night. They live in small groups made up of a monogamous couple and their offspring. The area is marked with scent glands, it is very small and overlaps with that of other groups.
Fruits are the main component of the diet. In the rainy season they also consume seeds and nectar, in the dry season leaves as well as insects and their larvae play a more important role.
Reproduction
In October or November the female gives birth to a young after a gestation period of 125 to 130 days, twins are rare. Mainly the females are responsible for the rearing of the young, the males participate only to a small extent. The young animals are weaned after around 135 days and sexually mature after around 2 years.
Danger
The main threat to the Mongozmaki is the destruction and fragmentation of the habitat through forest clearing. In addition, there is hunting. The IUCN lists the species as "endangered" ( vulnerable ).
The only German owner is Berlin.
literature
- Nick Garbutt: Mammals of Madagascar. A Complete Guide. Yale University Press, New Haven CT et al. 2007, ISBN 978-0-300-12550-4 .
- Thomas Geissmann : Comparative Primatology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin et al. 2002, ISBN 3-540-43645-6 .
supporting documents
Web links
- Information and pictures at arkive.org
- Eulemur mongoz onthe IUCN Red List of Threatened Species . Retrieved March 25, 2009.