Bowen's disease
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| D00 | Carcinoma in situ of the oral cavity, esophagus, and stomach |
| D00.0 | Lip, oral cavity and pharynx |
| D01 | Carcinoma in situ of other and unspecified digestive organs |
| D01.3 | Anal canal and anus |
| D04 | Carcinoma in situ of the skin |
| D07 | Carcinoma in situ of other and unspecified genital organs |
| D07.1 | vulva |
| D07.4 | Penile erythroplasia Queyrat onA |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
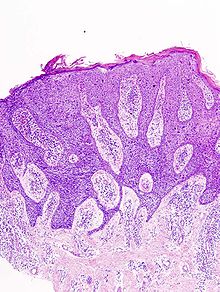
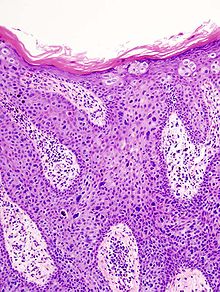
The Bowen's disease , also: dermatosis praecancerosa Bowen, Bowen carcinoma (Bowen's skin cancer), Erythroplasia de Queyrat (see below), dyskeratosis maligna is called intra- epidermal carcinoma in situ a precursor refers to a malignant tumor, in this case of squamous cell carcinoma ( formerly spinalioma , squamous cell cancer). This classification is controversial because the cells are already malignantly changed and have not yet broken through the basal cell membrane. The skin changes can be triggered by sunlight, chemical substances ( arsenic ) and certain viruses ( HPV ). The disease is named after John T. Bowen , who first described it. Bowen's disease is a disease of the second half of life and is slightly more common in men than women. In addition to actinic keratosis , it is another important precancerous condition of the skin.
Symptoms
Individual, sharply delimited but irregularly shaped, broad, red, scaly skin changes (erythrosquamous or psoriasiform plaques) appear on the skin. The size varies from millimeters to decimeters. The skin changes are similar to psoriasis (psoriasis), but usually only a fixed focus occurs.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is usually made on the basis of a tissue examination . In the enlarged epidermis there are atypical cells with a tendency to single cornification. The basement membrane is intact (otherwise one has to assume a carcinoma).
treatment
If possible, the healthy tissue should be surgically excised. A histological examination of the cutting edge is then carried out and, if necessary, re-excised.
Photodynamic therapy is also promising .
Queyrat erythroplasia
The erythroplasia of Queyrat is a carcinoma in situ of the mucous membranes, and transition mucous membranes, such. B. oral mucosa, anal region, glans and foreskin of the penis , vulva .
It is usually a single, erosive, easily vulnerable lesion. The transition to metastatic carcinoma is rapid. Histological diagnosis and therapy largely correspond to Bowen's disease. Due to the often unfavorable localization, surgical removal is often not (completely) possible, in which case radiation therapy is usually used. Since Queyrat's erythroplasia prefers lymphogenous metastasis, the nearest lymph node stations must be checked regularly for daughter tumors - especially if the lesion is not completely removed.
literature
- Ingrid Moll: Dual Dermatology Series . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2005
- Dr. med. Dirk Hasselmann: Light skin cancer: Recognize. To treat. Protect oneself. 1st edition. ISBN 978-3-7450-4315-0
Web links
- Macroscopic images of Bowen's disease in DermIS