Neber-Bössel synthesis
The Neber-Bössel synthesis is a name reaction in organic chemistry that goes back to the German chemist Peter Neber (1883–1960) and his colleague G. Bössel. The reaction was first published in 1929 for the synthesis of 3-hydroxylcinnoline.
Overview reaction
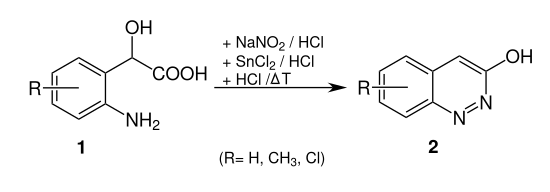
In the Neber-Bössel synthesis z. B. 2- (2-aminophenyl) -2- hydroxyacetic acid ( 1 , R = H) converted to 3-hydroxylcinnoline ( 2 , R = H).
Reaction mechanism
A possible reaction mechanism for the Neber-Bössel synthesis is described by Zerong Wang as follows:
2- (2-aminophenyl) -2-hydroxyacetic acid ( 1 ) is first reacted with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid in a diazotization reaction to give the diazonium salt 2 . With tin dichloride (SnCl 2 ) the reduction to the hydrazine derivative takes place , which under acid catalysis cyclizes to the hydrazide compound . Intermediate stage 3 produces 3-hydroxylcinnoline ( 4 ) through renewed elimination of water and deprotonation with aromatization .
application
The Neber-Bössel synthesis is used in preparative chemistry for the synthesis of cinnoline derivatives.