Cinnoline
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cinnoline | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 6 N 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless needles |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 130.15 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
40-41 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
114 ° C (0.4 hPa ) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Cinnoline is an organic compound that belongs to the heterocycles (more precisely: heteroaromatics and diazanaphthalenes ). The compound consists of a benzene ring to which a pyridazine ring is fused . Cinnoline is isomeric to quinazoline , quinoxaline and phthalazine .
Manufacturing
The synthesis of cinnoline is achieved through the electrolysis of (2-nitrophenethyl) propylamine. The reaction is carried out in a buffered mixture of methanol and water and gives cinnoline in moderate yield:
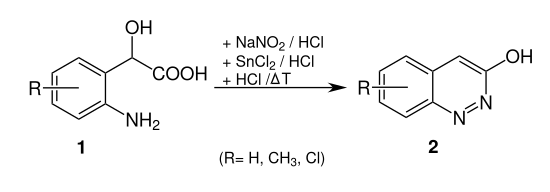
Cinnoline derivatives can also be produced using the Neber-Bössel synthesis . It is z. B. 2- (2-aminophenyl) -2- hydroxyacetic acid ( 1 , R = H) converted to 3-hydroxylcinnoline ( 2 , R = H):
Derivatives
Cinnoline is the starting structure for many derivatives.
- Cinnoline hydrochloride C 8 H 6 N 2 · HCl, CAS number: 5949-24-6
- Cinnoline-4-carboxylic acid C 9 H 6 N 2 O 2 , CAS number: 21905-86-2
- 4 (1 H ) -Cinnolinone C 8 H 6 N 2 O, CAS number: 18514-84-6
- Benzo [ c ] cinnoline C 12 H 8 N 2 , CAS number: 34524-78-2
- Cinoxacin (an antibiotic )
Individual evidence
- ↑ M. Busch, A. Rast: Ueber das Cinnolin. , Chem. Ber. , 1897 , 30 , pp. 521-527 ( doi : 10.1002 / cber.189703001103 ).
- ↑ a b J. S. Morley: Cinnolines. Part XX VII. The Preparation and Nitration of Cinnoline. , J. Chem. Soc. , 1951 , pp. 1971-1975.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ BA Frontana-Uribe, C. Moinet, L. Toupet, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1999 , 2 , 419-430.
- ^ Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, Volume 2 . John Wiley, Hoboken (NJ) 2009, ISBN 978-0-470-28662-3 , pp. 2022-2024 .
- ↑ Cinnoline derivatives at Chemicalland21 .