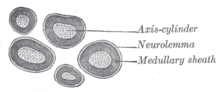
Neurilemm
The neurilemm (also neurolemma ) is the outermost layer of the cytoplasm of Schwann cells , which surrounds the axons of neurons . It forms the outermost layer of nerve fibers in the peripheral nervous system .
The neurolemma is underlain by the basement membrane. In the central nervous system , the axons are myelinated by the oligodendrocytes and therefore have no neurolemma. The myelin sheaths of oligodendrocytes do not have a neurolemm because the excess cytoplasm is directed to the cell body of the oligodendrocyte.
The neurolemma has a protective function for peripheral nerve fibers. Damaged nerve fibers can be regenerated if the perikaryon and neurolemma are intact. The neurolemma forms a stabilizing sheath through which the growing axon can restore its original connection.
A neurilemoma is a tumor of a neurolemma.
literature
- Siegmund von Schumacher: Outline of the human histology. Springer, Berlin 1943. (Reprint: ISBN 978-3-662-36085-9 )
Individual evidence
- ↑ Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn: Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7th edition. Pearson Benjamin Cummings, San Francisco 2007, ISBN 978-0-8053-5909-1 , pp. 394-395.
- ↑ neurilemoma ( Memento of 16 June 2009 at the Internet Archive ) In: Dorland's Medical Dictionary.