Pizza theorem
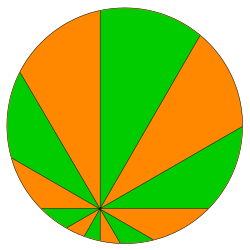
The Pizza Theorem is a mathematical theorem in plane geometry . It describes an equality of area that arises when the circle is broken down into partial areas.
If you lay straight lines ( ) through any inner point of a circle , so that two adjacent straight lines each intersect at an angle of , then you get a division of the circle into areas . If these are numbered clockwise, the sum of the areas with even numbers is equal to the sum of the areas with odd numbers.
The name of the theorem comes from the cutting technique used to cut a round pizza into pieces. If you place the knife at any other point on the pizza instead of at the center, you have exactly the above situation.
literature
- Wolfgang Kroll, Joachim Jäger: The Pizza Theorem . (PDF) In: Mathematica Didactica , Volume 33, 2010
- Rick Mabry, Paul Deiermann: Of Cheese and Crust: A Proof of the Pizza Conjecture and Other Tasty Results . (PDF; 185 kB) In: The American Mathematical Monthly , Volume 116, No. 5 (May, 2009), pp. 423–438 (English) ( JSTOR 40391118 )
- Larry Carter, Stan Wagon: Proof without Words: Fair Allocation of a Pizza . In: Mathematics Magazine , Vol. 67, No. 4 (Oct. 1994), p. 267
Web links
Commons : Pizza Theorem - collection of images, videos and audio files
- Eric W. Weisstein : Pizza Theorem . In: MathWorld (English).
- Sourcebook for pizza theorem (English)