Pristinamycins
Pristinamycins are a group of antibiotic substances that arise in the secondary metabolism of a number of species of Streptomyces and Actinoplanes . They have been known since the late 1950s. Pristinamycins are among the streptogramins .
structure
The pristinamycins are divided into two groups, the pristinamycins I and II the pristinamycins I belong to the group of B streptogramins, the branched cyclo. Hexa depsipeptide from the class of peptide - antibiotics represent. The pristinamycins II belong to the group of A-streptogramins, which are polyunsaturated macrolactones and belong to the group of polyketides . The individual compounds of each group differ slightly in some substituents, functional groups or amino acid components.
| Pristinamycin IA | Pristinamycin IB | Pristinamycin IC | Pristinamycin IIA | Pristinamycin IIB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
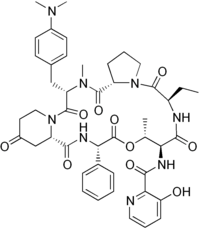 |
 |

|
||
| CAS No .: 3131-03-1 | CAS No .: 21411-53-0 | CAS No .: 21102-49-8 | ||
| Synonyms: Streptogramin B |
Synonyms: Ostreogrycin B 2 |
Synonyms: Ostreogrycin B 1 |
Synonyms: Virginiamycin M 1 |
Synonyms: Virginiamycin M 2 |
Effect and biosynthesis
Both groups of substances have bacteriostatic activity by blocking bacterial protein synthesis . In combination, however, the components work synergistically, with the activity increasing by a hundredfold and the effect ultimately being bactericidal. Pristinamycin I and pristinamycin II are produced in a ratio of about 30:70 by Streptomyces pristinaespiralis . This naturally occurring substance is used as a medicinal substance to treat infections with correspondingly sensitive germs.
The pristinamycin biosynthesis gene cluster is the largest known antibiotic supercluster with around 210 kb . Within this gene region, the genes that code for the biosynthesis of pristinamycin I and II are not clustered together, but are scattered over the entire 210 kb region. Furthermore, the biosynthetic gene region is interrupted by a cryptic type II polyketide biosynthetic gene cluster.
Derivatives
The partially synthetic, more water-soluble derivatives of pristinamycin, quinupristin and dalfopristin , are used as a fixed combination in the treatment of infections with multi-resistant pathogens - e.g. B. Vancomycin Resistant Strains (VRSA) - used. The combination of two further partially synthetic derivatives, flopristin and linopristin , is being developed with the same indication .
Web links
- Quentin Ravelli: The Pill Roll . In: Le monde diplomatique . January 9, 2015.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b J.-M. Paris et al: The Chemistry of Pristinamycins. In: G. Lucas, M. Ohno (Eds.): Recent Progress in the Chemical Synthesis of Antibiotics. Springer Verlag, 1990, pp. 185 ff.
- ↑ Y. Mast, T. Weber, M. Gölz, R. Ort-Winklbauer, A. Gondran, W. Wohlleben, E. Schinko: Characterization of the 'pristinamycin supercluster' of Streptomyces pristinaespiralis. In: Microbial Biotechnology. 2011. doi: 10.1111 / j.1751-7915.2010.00213.x .