Diamond pit
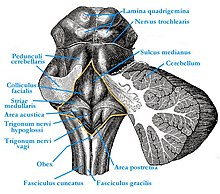
The diamond pit (Latin fossa rhomboidea ) is the diamond-shaped floor of the 4th ventricle in the area of the brain stem . It is laterally bounded by the cerebellar stalks ( pedunculi cerebellares ), the tuberculum cuneatum and the tuberculum nuclei gracilis , the bottom is formed by the back surfaces of the pons and medulla oblongata . The diamond pit was named Calamus scriptorius as early as the 3rd century BC. Described by the Greek doctor Herophilos of Chalcedon . The term 'Calamus scriptorius' is used today for the pen-like pointed tip at the end of the diamond pit.
In the area of the lozenge pit in the brain stem there are important core areas for circulatory regulation and the cranial nerves as well as ascending and descending pathways.
Structures of the diamond pit
The diamond pit is divided into two halves by a central channel ( sulcus medianus ). There is a flat elevation on both sides of the midline, the eminentia medialis . The facial mound ( colliculus facialis ), which is formed by the inner knee of the facial nerve and the abducent nucleus, bulges out in the middle . Caudally, the eminentia medialis ends in the small hypoglossal triangle ( Trigonum nervi hypoglossi ), which is formed by the nucleus nervi hypoglossi , the core area of the nervus hypoglossus . The vagus triangle ( Trigonum nervi vagi , syn. Ala cinerea ) lies to the side of the hypoglossal triangle, delimited by a small separating furrow ( sulcus limitans ). This is where the sensitive core area of the vagus nerve and the glossopharyngeal nerve are located . A thickened ependymal strip , funiculus separans , separates the vagus triangle from the area postrema . The latter belongs to the circumventricular organs and contains, among other things, the vomiting center . To the side and rostral of the area postrema is the area acustica , in which the cochlear nuclei of the vestibulocochlear nerve lie. The medullary stripes ( Striae medullares ) belong to the auditory pathway . Laterally in the upper third of the lozenge pit is the Locus caeruleus , an elongated structure that shimmers bluish through pigmented nerve cells .
At the rear end of the diamond pit, the bolt ( obex ) rises . This structure, along with parts of the brain stem, is taken from cattle when slaughtered for testing for BSE .
Individual evidence
- ↑ JG Chusid: Functional Neurology: Anatomical, Diagnostic and Clinical Basics . Springer, Berlin 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-06422-1 , pp. 48 .
- ^ Larry Swanson, Neuroanatomical Terminology: A Lexicon of Classical Origins and Historical Foundations . Oxford University Press, 2014, ISBN 978-0-19-021146-2 .
- ^ A b H. Frick, H. Leonhardt, D. Starck: Spezial Anatomie . tape 2 . Georg Thieme, Stuttgart 1992, ISBN 978-3-13-356904-0 , p. 276 .
- ↑ World Organization for Animal Health: Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (PDF)