Hypoglossal nerve
The paired hypoglossal nerve (from ancient Greek γλῶσσα glōssa 'tongue' and ὑπό hypó 'under') is also called the twelfth cranial nerve , N. XII or the tongue muscle nerve . It is responsible for the motor innervation of the tongue .
course
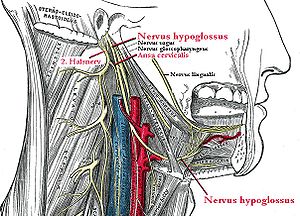
The nucleus of the nerve - nucleus nervi hypoglossi - is located in the medulla oblongata , visible in the diamond pit as the trigonum n. Hypoglossi above the trigonum n. Vagi . The nerve reaches the surface of the brain in the sulcus praeolivaris and leaves the cranial cavity through the canalis nervi hypoglossi . Then the nerve runs in the parapharyngeal space , later in the carotid trigonum . Ventral branches of the upper cervical nerves, which later form the upper root of the ansa cervicalis , attach to it briefly. The hypoglossus nerve itself enters the tongue from the underside of the tongue between the hyoglossus and mylohyoid muscles through the lateral sulcus linguae and innervates the internal and external tongue muscles .
Hypoglossal palsy
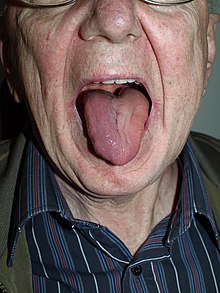
Unilateral damage to the nerve leads to one-sided paralysis of the tongue with deviation to the diseased side. Difficulties in eating and drinking and articulation disorders can occur. Damage on both sides leads to complete paralysis of the tongue, longer damage to atrophy of the tongue muscles.
In animals, nerve function can be tested by pulling out the tongue, assessing the force with which the animal tries to pull the tongue back. In dogs , you can simply moisten the nose, and the animal will usually try to lick it off.
In Jackson syndrome (cranial nerve syndrome) , in addition to lesions of the hypoglossal nerve, damage to the vagus nerve and the accessory nerve occurs .
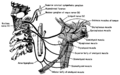
Schematic representation of the innervation areas of the hypoglossal nerve.
supporting documents
- ^ Alfred Goldschmid: III head: 2.1 Neurocranium. In: W. Westheide, R. Rieger: Special Zoology. Part 2. Vertebrate or skull animals. Spektrum, Munich 2015, ISBN 3-8274-0307-3 , p. 37.
literature
- Martin Trepel: Neuroanatomy. Structure and function. 3rd, revised edition. Urban & Fischer, Munich et al. 2004, ISBN 3-437-41297-3 .
- Franz-Viktor Salomon: nervous system, systema nervosum . In: Franz-Viktor Salomon, Hans Geyer, Uwe Gille (Ed.): Anatomy for veterinary medicine. Enke, Stuttgart 2005, ISBN 3-8304-1007-7 , pp. 464-577.
- Hamid Emminger, Thomas Kia (ed.): Exaplan. The Compendium of Clinical Medicine. Volume 1. 6th edition. Elsevier, Urban & Fischer, Munich 2010, ISBN 978-3-437-42463-2 .