Nucleus nervi hypoglossi

The nucleus nervi hypoglossi ( Latin nucleus of the hypoglossus nerve ), or Nucl. n. hypoglossi , is a pair of cranial nerve kernels ( nucleus , "core") in the elongated medulla (medulla oblongata) , a part of the brain . It consists of nerve cell bodies with their processes, the so-called axons , the associated XII. Form cranial nerve . This is called the hypoglossal nerve .
The left hypoglossal nerve emerges from the left hypoglossal nerve, and the right hypoglossal nerve emerges from the right. The two XII. Cranial nerves are responsible for the supply ( innervation ) of the entire tongue muscles .
Neuroanatomy
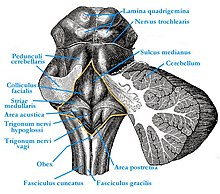
The hypoglossal nerve, whose axons originate in the associated core area, is a purely motor nerve that supplies the tongue muscles. The innervation can be arbitrary. The nucleus nervi hypoglossi is therefore a purely somatomotor core area.
The nucleus nervi hypoglossi lies in the rear part of the diamond pit , which is the diamond-shaped floor of the 4th ventricle in the area of the brain stem , in the area of the hypoglossal triangle ( Trigonum nervi hypoglossi ). Nerve fibers from the motor cerebral cortex (the part of the brain in which conscious motor movements are controlled) of the mutual (contralateral) hemisphere pull to the core area . The nerve fibers emanating from the core area leave the brain stem between the pyramid and olive .
The rami medullares are responsible for the blood supply to the nucleus nervi hypoglossi . These are branches of the anterior spinal artery , an unpaired vessel that emerges from the left and right vertebral arteries .
development
Since the nucleus is located superficially and centrally on the brain stem, it is, like all other somatomotor nuclei, a derivative of the baseplate (attachment of the motor areas in the brain) of embryonic development.
Clinical references
Unilateral damage to the nucleus nervi hypoglossi, like damage to the associated cranial nerve, leads to paralysis of parts of the tongue muscles. The tongue deviates to the side of the damage when it protrudes (for details, see the article Hypoglossal nerve ). Damage to the core area results in slurred, indistinct speech ( dysarthria ) . Besides, it can dysphagia come. Since both cores are relatively close to each other, damage to both cores is possible.
The nucleus nervi hypoglossi can be damaged by cerebral infarction as a result of vascular occlusion. A closure of the rami medullares supplying the core area leads to the so-called medial medulla oblongata syndrome ( Déjerine syndrome ). Involvement of this core area is also typical in other rare brainstem syndromes, e.g. B. in Tapia and Schmidt syndrome .
literature
- Werner Kahle, Michael Frotscher: Pocket Atlas Anatomy. Volume 3: Nervous System and Sense Organs. 10th, revised edition. Georg Thieme Verlag et al., Stuttgart et al. 2009, ISBN 978-3-13-492110-6 .
- Kurt Stoschitzky: ÖH script: Central nervous system and cranial nerves. Service company ÖH-Uni Graz GmbH.
Web links
- Neuroassistant Basics : Nucleus nervi hypoglossi - Interactive mapping of the brain stem with a view of the diamond pit and representation of the location of the cranial nerve nuclei.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Martin Trepel : Neuroanatomy. Structure and function. 4th, revised edition. Elsevier, Urban & Fischer Verlag, Munich / Jena 2008, ISBN 978-3-437-41298-1 , p. 139.
- ↑ a b Peter P. Urban (Ed.): Diseases of the brain stem. Clinic, diagnostics, therapy. Schattauer, Stuttgart 2009, ISBN 978-3-7945-2478-5 , p. 33.
- ↑ Martin Trepel: Neuroanatomy. Structure and function. 4th, revised edition. Elsevier, Urban & Fischer Verlag, Munich / Jena 2008, ISBN 978-3-437-41298-1 , p. 86.
- ^ Andreas Hufschmidt, Carl Hermann Lücking, Sebastian Rauer (Eds.): Neurologie compact. For clinic and practice. 5th, updated and expanded edition. Thieme, Stuttgart et al. 2009, ISBN 978-3-13-117195-5 , p. 59.