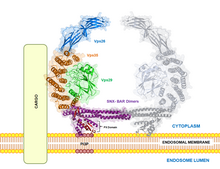
Retromer
A retromer is a protein complex that is involved in the transport of membrane proteins in vesicles between endosomes and the trans -Golgi network .
construction
In mammalian cells, retromers consist of five different proteins (a heteropentamer ), including a heterodimer from two of the sorting Nexins SNX1 , SNX2 , SNX5 and SNX6 and a heterotrimer from Vps26 , Vps29 and Vps35 ( vacuolar protein sorting ). They serve simultaneously as a membrane-stabilizing protein framework and as a sorting signal. Retromers are involved in transport within the cell, in signal transduction during development and in the formation of lysosomes . In polarized cells such as epithelial cells and neurons , the retromer is also used for transcytosis . In yeast , a retromer consists of the five proteins Vps5, Vps17, Vps26, Vps29 and Vps35. The subunit Vps35 binds various cellular membrane proteins for sorting. A heterodimer made from SNX1 or SNX2 with SNX5 or SNX6 induces the bulging of the endosome membrane into a tubular membrane structure from which transport vesicles are tied off. The constriction of a vesicle from the tubular protuberance is mediated not only by actin polymerization but also by Dynamin-II or EHD1 .
Sorting
The sorting on the retromer determines whether a bound membrane protein remains in the endosome and later degradation in the lysosome or whether it is transported from the endosome into the trans-Golgi network near the cell membrane . Vps 35 binds the WASH protein complex (more precisely FAM21 and WASH1 ). Sorting into different vesicles requires sorting the membrane proteins into different areas of the endosome membrane, where a tubular protuberance of the endosome membrane takes place to form transport vesicles. The membrane proteins to be sorted bind to the trimeric subunit Vps35-Vps29-Vps26 of the retromer (the cargo-selective complex , CSC).
The proteins in the endosome membrane are sorted by binding the WASH complex, which activates Arp2 / 3 on the cytosolic side of the endosome membrane . This creates actin filaments that mediate a sideways movement of the retromer and its loading (bound membrane proteins) in the endosome membrane. The binding of the trimeric subunit Vps35-Vps29-Vps26 to the membrane proteins to be sorted takes place in their cytosolic regions. GTP -activated Rab7 , clathrin , clathrin adapter proteins and other proteins then binds .
Assorted proteins
More than 100 membrane proteins are sorted by the retromer. Disturbance of the retro-merger significantly reduces the amount of these proteins in the cell membrane. The sorted proteins include M6PR (synonym CIMPR), GPR177 , Sortilin 1 , DMT1-II (synonym Slc11a2), Wntless (synonym MIG-14), Crumbs and a still unknown protein that transports amyloid precursor protein .
Pathogens
Bacteria living intracellularly in vesicles have developed various mechanisms to inhibit vesicle transport. The RidL protein from Legionella pneumophila inhibits the retromere, while IncE from Chlamydia trachomatis inhibits SNX5 / 6.
Applications
Retromers are being investigated for the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b C. Trousdale, K. Kim: Retromer: Structure, function, and roles in mammalian disease. In: European journal of cell biology. Volume 94, number 11, November 2015, pp. 513-521, doi : 10.1016 / j.ejcb.2015.07.002 , PMID 26220253 .
- ↑ JJ Liu: Retromer-Mediated Protein Sorting and vesicular trafficking. In: Journal of genetics and genomics = Yi chuan xue bao. Volume 43, number 4, April 2016, pp. 165–177, doi : 10.1016 / j.jgg.2016.02.006 , PMID 27157806 .
- ↑ M. Vergés: Retromer in Polarized Protein Transport. In: International review of cell and molecular biology. Volume 323, 2016, pp. 129-179, doi : 10.1016 / bs.ircmb.2015.12.005 , PMID 26944621 .
- ^ Seaman MN: Cargo-selective endosomal sorting for retrieval to the Golgi requires retromer . In: The Journal of Cell Biology . 165, No. 1, Apr 2004, pp. 111-22. doi : 10.1083 / jcb.200312034 . PMID 15078902 . PMC 2172078 (free full text).
- ↑ Shimada A, Niwa H, Tsujita K, Suetsugu S, Nitta K, Hanawa-Suetsugu K, Akasaka R, Nishino Y, Toyama M, Chen L, Liu ZJ, Wang BC, Yamamoto M, Terada T, Miyazawa A, Tanaka A. , Sugano S, Shirouzu M, Nagayama K, Takenawa T, Yokoyama S: Curved EFC / F-BAR-domain dimers are joined end to end into a filament for membrane invagination in endocytosis . In: Cell . 129, No. 4, May 2007, pp. 761-72. doi : 10.1016 / j.cell.2007.03.040 . PMID 17512409 .
- ↑ Bhatia VK, Madsen KL, Bolinger PY, Kunding A, Hedegård P, Gether U, Stamou D: Amphipathic motifs in BAR domains are essential for membrane curvature sensing . In: The EMBO Journal . 28, No. 21, Nov 2009, pp. 3303-14. doi : 10.1038 / emboj.2009.261 . PMID 19816406 . PMC 2776096 (free full text).
- ↑ Walseng E, Bakke O, Roche PA: Major histocompatibility complex class II-peptide complexes internalize using a clathrin- and dynamin-independent endocytosis pathway . In: The Journal of Biological Chemistry . 283, No. 21, May 2008, pp. 14717-27. doi : 10.1074 / jbc.M801070200 . PMID 18378669 . PMC 2386912 (free full text).
- ^ M. Gallon, PJ Cullen: Retromer and sorting nexins in endosomal sorting. In: Biochemical Society transactions. Volume 43, number 1, February 2015, pp. 33-47, doi : 10.1042 / BST20140290 , PMID 25619244 .
- ↑ MN Seaman, A. Gautreau, DD Billadeau: Retromer-mediated endosomal protein sorting: all WASHed up! In: Trends in cell biology. Volume 23, number 11, November 2013, pp. 522-528, doi : 10.1016 / j.tcb.2013.04.010 , PMID 23721880 , PMC 3924425 (free full text).
- ↑ a b c d M. N. Seaman, A. Gautreau, DD Billadeau: Retromer-mediated endosomal protein sorting: all WASHed up! In: Trends in cell biology. Volume 23, number 11, November 2013, pp. 522-528, doi : 10.1016 / j.tcb.2013.04.010 , PMID 23721880 , PMC 3924425 (free full text).
- ↑ Nothwehr SF, Ha SA, Bruinsma P: Sorting of yeast membrane proteins into an endosome-to-Golgi pathway involves direct interaction of their cytosolic domains with Vps35p . In: The Journal of Cell Biology . 151, No. 2, Oct 2000, pp. 297-310. doi : 10.1083 / jcb.151.2.297 . PMID 11038177 . PMC 2192648 (free full text).
- ↑ Rojas R, van Vlijmen T, Mardones GA, Prabhu Y, Rojas AL, Mohammed S, Heck AJ, Raposo G, van der Sluijs P, Bonifacino JS: Regulation of retromer recruitment to endosomes by sequential action of Rab5 and Rab7 . In: The Journal of Cell Biology . 183, No. 3, Nov 2008, pp. 513-26. doi : 10.1083 / jcb.200804048 . PMID 18981234 . PMC 2575791 (free full text).
- ^ McGough IJ, Cullen PJ: Recent advances in retromer biology . In: Traffic . 12, No. 8, Aug 2011, pp. 963-71. doi : 10.1111 / j.1600-0854.2011.01201.x . PMID 21463457 .
- ^ A b F. Steinberg, M. Gallon, M. Winfield, EC Thomas, AJ Bell, KJ Heesom, JM Tavaré, PJ Cullen: A global analysis of SNX27-retromer assembly and cargo specificity reveals a function in glucose and metal ion transport . In: Nature cell biology. Volume 15, number 5, May 2013, pp. 461-471, doi : 10.1038 / ncb2721 , PMID 23563491 , PMC 4052425 (free full text).
- ↑ Arighi CN, Hartnell LM, Aguilar RC, Haft CR, Bonifacino JS: Role of the mammalian retromer in sorting of the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor . In: The Journal of Cell Biology . 165, No. 1, Apr 2004, pp. 123-33. doi : 10.1083 / jcb.200312055 . PMID 15078903 . PMC 2172094 (free full text).
- ↑ Belenkaya TY, Wu Y, Tang X, Zhou B, Cheng L, Sharma YV, Yan D, Selva EM, Lin X: The retromer complex influences Wnt secretion by recycling wntless from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network . In: Developmental Cell . 14, No. 1, Jan 2008, pp. 120-31. doi : 10.1016 / j.devcel.2007.12.003 . PMID 18160348 .
- ↑ Canuel M, Korkidakis A, Konnyu K Morales CR: sortilin mediates the lysosomal targeting of cathepsins D and H . In: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications . 373, No. 2, Aug 2008, pp. 292-7. doi : 10.1016 / j.bbrc.2008.06.021 . PMID 18559255 .
- ↑ a b c d M. N. Seaman: The retromer complex - endosomal protein recycling and beyond. In: Journal of cell science. Volume 125, Pt 20 October 2012, pp. 4693-4702, doi : 10.1242 / jcs.103440 , PMID 23148298 , PMC 3517092 (free full text).
- ↑ a b N. Personnic, K. Bärlocher, I. Finsel, H. Hilbi: Subversion of Retrograde Trafficking by Translocated Pathogen Effectors. In: Trends in microbiology. Volume 24, number 6, June 2016, pp. 450-462, doi : 10.1016 / j.tim.2016.02.003 , PMID 26924068 .
- ↑ C. Li, SZ Shah, D. Zhao, L. Yang: Role of the Retromer Complex in Neurodegenerative Diseases. In: Frontiers in aging neuroscience. Volume 8, 2016, p. 42, doi : 10.3389 / fnagi.2016.00042 , PMID 26973516 , PMC 4772447 (free full text).
- ^ S. Wang, HJ Bellen: The retromer complex in development and disease. In: Development. Volume 142, number 14, July 2015, pp. 2392-2396, doi : 10.1242 / dev.123737 , PMID 26199408 , PMC 4510866 (free full text).