Riemschneider reaction
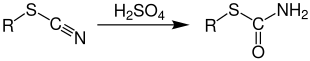
The Riemschneider reaction , named after the German chemist Randolph Riemschneider , is a name reaction from the field of organic chemistry and was first described in 1949. The Riemschneider reaction enables thiocarbamates (also called thiourethanes ) to be prepared from thiocyanates using concentrated sulfuric acid and an alcohol or olefin .
Overview reaction
Thiocyanates react with concentrated sulfuric acid and subsequent processing with ice water to give thiocarbamates :
The addition of an alcohol which is stable in concentrated sulfuric acid, however, enables the preparation of N -substituted thiocarbamates:
The alcohols or olefins used are preferably secondary alcohols, tertiary alcohols and olefins which are stable in concentrated sulfuric acid.
Reaction mechanism
The following reaction mechanism is described in the literature:
Protonation of thiocyanate 1 results in the formation of carbocation 2 . Intermediate stage 3 is formed by addition and subsequent intra-molecular rearrangement , from which, by deprotonation, the N -substituted thiocarbamate 4 is formed.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents , Wiley, 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , pp. 2392-2394.
- ↑ R. Riemschneider and O. Lorenz: Mitt. XI: About the mechanism of the conversion of rhodanides with conc. Sulfuric In: Journal of Nature Research B . 10, 1955, pp. 181-183, doi: 10.1515 / znb-1955-0401 .
- ^ R. Riemschneider, F. Wojahn, and G. Orlick: Thiocarbamates. III.1 Aryl Thiocarbamates from Aryl Thiocyanates In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . 73, 1951, pp. 5905-5907, doi: 10.1021 / ja01156a552 .
- ↑ a b R. Riemschneider: Thiocarbamates and Related Compounds. X.1 a New Reaction of Thiocyanates In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . 78, 1956, pp. 844-847, doi: 10.1021 / ja01585a038 .