Black hair tongue
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| K14.3 | Hypertrophy of the papillae of the tongue |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
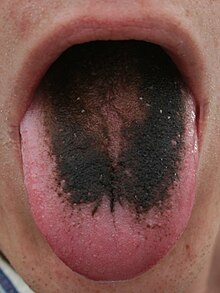
A disease of the tongue is called black hairy tongue , also known as nigrities linguae or lingua villosa nigra (also called lingua nigra ) . The hairy tongue should not have a disease value in the true sense of the word. It is found in 3% of the population, mainly men.
It is caused by the elongation of certain papillae (papillae filiformes) of the tongue, which form a hairy and usually dark coating on the back of the tongue. Depending on the food consumed, the tongue takes on a dark green to blackish color. The expansion of the tongue coating can reach very far back into the throat. There it causes an extremely uncomfortable, annoying tickling when speaking and swallowing, and sometimes gagging. The hairy tongue often disappears on its own after a few weeks or months.
The cause of the disease is unknown. A change in the oral cavity flora is suspected, e.g. B. through antibiotic therapy , corticosteroids , tobacco smoking , niacin deficiency and various other substances, including in mouthwashes or mouthwashes (e.g. chlorhexidine ).
The treatment of hairy tongue is difficult. The focus is on removing any trigger. The use of a soft toothbrush, a tongue scraper, 40% urea solution or sucking on vitamin C tablets can be helpful as symptomatic therapy .
See also
- Coated tongue
- Lingua plicata
- Raspberry tongue for scarlet fever
- Lacquer tongue
- Leukoplakia
- Hunter glossitis in pernicious anemia
literature
- K. Bork, W. Burgdorf, N. Hoede: Oral mucous membrane and lip diseases: Clinic, diagnostics and therapy. Schattauer; 3rd edition 2008. ISBN 978-3-7945-2486-0
- S. Dimitrios, P. Maria-Aikaterini u. a .: Lingua villosa nigra. In: Internal medicine. Volume 51, Number 11, 2012, p. 1453, ISSN 1349-7235 . PMID 22687867 .
- Z. Sheikh, AS Khan, S. Khan: Lingua villosa nigra. In: Lancet. Volume 377, Number 9772, April 2011, pp. 1183, ISSN 1474-547X . doi: 10.1016 / S0140-6736 (10) 60930-0 . PMID 21440293 .