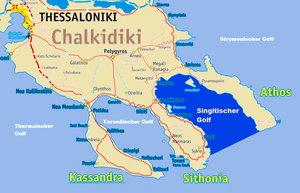
Singitian Gulf
| Singitischer Gulf Singitikós Kólpos, Gulf of Monte Santo |
|
|---|---|
| Waters | Aegean Sea |
| Land mass | Chalkidiki |
| Geographical location | 40 ° 11 ′ N , 24 ° 0 ′ E |
| width | 24 km |
| depth | 48 km |
| Greatest water depth | 521 m |
The Singitian Gulf ( Greek Σιγγιτικός κόλπος , Singitikós Kólpos ) is an arm of the Aegean Sea . It separates the middle finger Sithonia of the Chalkidiki peninsula from the eastern finger, Mount Athos .
The name of the gulf goes back to the ancient city of Singos , the exact location of which is unclear. The gulf is named after Mount Athos as the gulf of Hagion Oros ( Greek Κόλπος Αγίου Όρους ) or as the gulf of Monte Santo .
The Persian great king Xerxes I had the Xerxes Canal built around 480 BC at the narrowest point of the isthmus of the Athos peninsula , which leads from the Gulf of Ierissos in the north to the Singitian Gulf immediately west of the town of Trypiti, which he used during his campaign in the Persian War allowed passage through the sheltered gulf.
The Singitische Gulf, which runs from northwest to southeast, is 24 km wide, 48 km long and up to 521 m deep.