Current mode logic
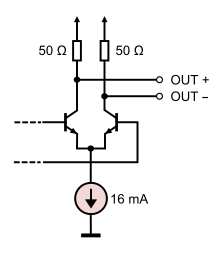
The English term Current Mode Logic (short: CML , German Stromschaltlogik ), also English Source Coupled Logic (short: SCL , German roughly source- coupled logic ), in digital technology, is an interface standard for cable-based high-speed Data transfers with bit rates between 312.5 Mbit / s to 12.5 Gbit / s. CML is comparable to the transmission standard Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS), but has a fixed line impedance of 50 Ω for the copper cables used . CML is standardized in the JEDEC standard JESD204.
In the context of network protocol layer models, CML describes the lowest physical bit transmission layer , not the higher protocol layers on top of it . CML is used in digital-to-analog converters and analog-to-digital converters with high data rates for data connection to digital logic circuits such as field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). Further applications are interfaces based on Transition-Minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS). Examples are Digital Visual Interface (DVI) and High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI). CML uses differential transmission on lines of defined wave impedance . Bipolar transistors in the linear operating range are used as active components ; the voltage difference between the two lines is nominally 800 mV.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Introduction to LVDS, PECL, and CML (HFAN-1.0). Maxim Integrated Circuits, April 2008, accessed April 30, 2014 .
- ↑ Serial Interface for Data Converters, JEDEC standard JESD204. JEDEC, April 2006, accessed April 30, 2014 (restricted access).
- ↑ JESD204B Survival Guide. Analog Devices - Technical Article, accessed April 30, 2014 .
- ↑ Digital Visual Interface & TMDS Extensions, White Paper. Silicon Image, 2004, accessed February 19, 2015 .