Spirometer
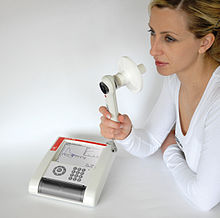
A spirometer is a medical device for measuring the volume of air inhaled or exhaled, called tidal volume , as well as the air volume flow and its change over time. It is used in spirometry to check lung function or vital capacity . Spirometry is the most commonly performed test in pulmonology .
history
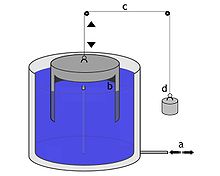
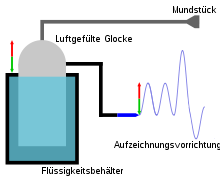
In the first spirometers, a gas-filled bell was placed on top of a liquid-filled and sealed flask. The patient inhaled and exhaled the air from the bell through a tube, as a result of which the gas volume within the bell changed and the pressure differences caused it to move upwards during exhalation (see fig. Red arrow) and downwards during inhalation (green arrow). These movements could be graphically documented as a progression curve using a suitable recording device such as a kymograph . A calibration , such as the use of exactly one liter of air in the bell, made it possible to calculate the lung volumes and their development over time.
Furthermore, lime can be used to remove carbon dioxide from the breathing air flowing in, which reduces the volume of the bell proportionally to the oxygen used by the test participant. The oxygen consumed can then be converted into the energy converted by the organism using indirect calorimetry .
Current spirometer
Nowadays the volume is only measured indirectly. The volume is integrated by measuring the flow velocity in the breathing tube. Common measuring methods today are turbine , pneumotachograph and ultrasound :
- The advantage of a turbine is the low price. Here, the volume is determined from the speed of a turbine in the breathing tube, but the measurement is sometimes imprecise, as the turbine only begins to rotate after a certain air flow has been reached or, if it is very well stored, it rotates slightly after the end.
- A pneumotachograph determines the flow speed via pressure differences in the breathing tube when the air flows through lamellae. It is initially very precise, but loses precision due to the soiling of the lamellas from the moisture in the air you breathe. Regular cleaning or replacement of the slats must be ensured.
- When using ultrasound , the difference in transit time between two ultrasound paths is evaluated, one with and one against the air flow. This method is the most accurate and does not require calibration of the device, since all influencing factors are the same for both measuring sections and thus cancel each other out during the measurement. Obtaining the technology is usually more expensive than the other methods described.
See also
- Peak flow meter
- Spirometry
- Lung function
literature
- Lundy Braun: Breathing Race into the Machine: The Surprising Career of the Spirometer from Plantation to Genetics . University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis 2014, ISBN 978-0-8166-8357-4 .
- Elias von Cyon : Spirometry and Pneumometry, In: Ders .: Methodik der Physiologische Experimente und Vivisectionen , p. 213. Giessen, St. Petersburg: Ricker, 1876 (available online: text , images on panel 27 , panel 28 , legend to the Panels )