Marginal lending facility
| interest rate | height |
|---|---|
| European Central Bank (valid from: September 18, 2019) | |
| Deposit rate (deposit facility) | −0.50% |
| Base rate (main refinancing operations) | 0.00% |
| Marginal lending rate (marginal lending facility) | 0.25% |
| Swiss National Bank (valid from: June 13, 2019) | |
| SNB policy rate | −0.75% |
| Federal Reserve System (effective March 16, 2020) | |
| Federal funds rate target range | 0.0 to 0.25% |
| Primary Credit Rate | 0.25% |
| Bank of Japan (effective December 19, 2008) | |
| Discount rate (basic discount / loan rate) | 0.30% |
| Bank of England (effective March 19, 2020) | |
| Official Bank Rate | 0.1% |
| Chinese People's Bank (valid from: February 20, 2020) | |
| Discount rate (one-year lending rate) | 4.05% |
A marginal lending facility ( SRF ) is a possibility for commercial banks in the euro area to raise money at short notice (overnight) from the European Central Bank (ECB). The price for using the SRF is the marginal lending rate ( SRS ) specified by the central bank . The SRF is thus an important monetary policy instrument of the ECB.
General
Until the European Central Bank (ECB) was founded in June 1998, the national European central banks, such as the Deutsche Bundesbank , provided their affiliated credit institutions with Lombard loans in exchange for lending on securities that could be bombarded as part of their monetary policy ( Lombard policy ). This enables the credit institutions to obtain the liquidity they need. The securities on loan must be owned by the credit institution ( deposit A ). At the Bundesbank, the granting of a Lombard loan to the credit institutions was limited to a term of three months. The interest rate on Lombard loans was called the Lombard rate and was an important indicator of the money market.
With the transfer of responsibility for monetary policy to the ECB, the marginal lending facility replaced the former Lombard loan in January 1999. According to Art. 18.1 of the ECB Statute, the ECB is authorized to enter into credit transactions with the affiliated credit institutions in return for “sufficient collateral”, so-called central bank-eligible collateral. Since January 2007, a uniform framework (“uniform list of collateral”) has been in place for eligible collateral, which includes marketable and non-marketable collateral. In the case of collateral eligible for a central bank, lending limits are applied depending on the liquidity categories, remaining terms and types of interest, as well as fluctuation margins, as is the case with Lombard loans.
execution
The initiative for marginal lending comes from the commercial banks. These are approved for transactions with the ECB, so they can at the central bank short-needed money by pledging of assets eligible as collateral ( securities procured). Due to the short- term nature of such transactions, this form of financing is also known as an overnight loan or overnight money.
If the bank has outstanding debit balances on the ESCB accounts at the end of the day , these automatically become marginal lending facilities. The price for using the SRF is the marginal lending rate (in some cases also the marginal lending facility rate and the marginal lending interest rate).
Marginal lending facilities are offered permanently and in unlimited volumes; therefore it is also known as the standing facility . The word facility (from Latin facilitas lightness) comes from banking English (facility) and describes the possibility of taking short-term loans or investing credit within specified limits.
classification
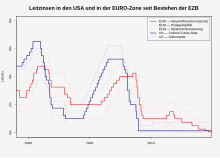
The marginal lending rate is commonly referred to as one of the three key ECB rates . The interest rate is set by the Governing Council and forms the upper limit of the interest rate corridor . As a rule, it is always one percentage point above the main refinancing rate. However, the ECB deviated from this shortly after the introduction of the euro and since the financial crisis from 2007 . The marginal lending is the counterpart of the deposit facility . Longer-term liquidity is made available to the banks primarily through the main refinancing instrument.
With the transfer of responsibility for monetary policy to the ECB, the marginal lending facility has replaced the former Lombard loan .
Importance for the money market
The SRF primarily fulfills two functions:
In contrast to the main refinancing business, the primary importance of this financing instrument lies in the fact that the commercial banks can procure liquidity of their own accord at any time and thus avoid liquidity bottlenecks. The purpose of this instrument is therefore primarily to secure liquidity for commercial banks and to comply with the legal requirements for minimum reserves .
Second, the SRF has a monetary policy significance: In principle, commercial banks can also obtain overnight loans via the money market ( interbank market ). However, overnight loans offered there must inevitably be cheaper (ie lower interest rates) than the SRF, since otherwise no transactions can be made on the interbank market. Therefore, the SRF forms the upper limit of the interest charged for overnight loans. If the ECB increases (decreases) the SRS, the commercial banks also increase (decrease) their interest rate for overnight loans - consequently, the SRS also serves to enforce interest rate policy on the market.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ For the term "peak lending rate" see Deutsche Bundesbank, permanent facilities, accessed on April 27, 2011 ( memento of the original from November 19, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Finanz-Lexikon, accessed April 27, 2011.