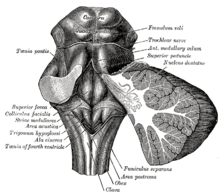
Striae medullares
When striae medullares (v. Lat. Stria "recess groove" medulla "Mark") strip-shaped anatomical structures in the marrow are referred to some organs. In the brain, they appear as white matter due to the strong myelination of the nerve fibers passing through them .
Striae medullares of the 4th ventricle
The striae medullares ventriculi quarti (also Striae acusticae posteriores) are fiber structures of the brain stem and lie on the anterior (rostral) wall of the 4th ventricle , which is formed by the posterior (dorsal) surface of the bridge (pons) . Aural nerve fibers run through them from the posterior auditory nucleus (nucleus cochlearis dorsalis) to the sulcus medianus in the hindbrain , where they join the lateral loop (lemniscus lateralis) .
Striae medullares of the thalamus
The striae medullares thalami are fiber structures of the diencephalon (diencephalon) and pull along the thalamus to Epithalamus . As a result, among other things, the afferents run from the olfactory brain to the Ncll. habenulares (habenular kernels) .