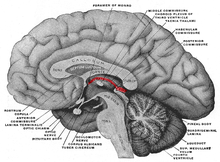
Epithalamus
The epithalamus is part of the interbrain ( diencephalon ). It lies dorsal to the thalamus on the III. Ventricle . Human anatomy (TA) belong to the epithalamus
next to the unpaired circumventricular organs
- Pineal gland (epiphysis, corpus pineale, glandula pinealis)
- Subcommissural organ (Organum subcommissurale)
and the mutually connecting fiber strands
- Commissura habenularum
- Commissura posterior (Commissura epithalamica)
on both sides the regional core areas of
- Habenulae (reins), as the nucleus habenularis medialis and lateralis
- Area pretectalis , with several differently delimited nuclei pretectales
The pineal gland or epiphysis occupies an intermediate position between the central nervous system and the endocrine organs in the classification of the organs . It plays an important role in the control of circadian (day-night) and seasonal rhythms and is therefore also part of the photoneuroendocrine system .
The habenulae or pedicels of the epiphyses contain thin fiber strands on each side by which the epiphysis is connected (in the continuation as stria medullaris thalami also with the thalamus ). In addition, the two nuclei habenulares are found here , which u. a. serve as a switching station for pathways of the olfactory system, which connect the olfactory brain with the autonomic centers in the brain stem . The habenula nuclei receive afferents from olfactory centers via the striae medullares (thalami) and additionally via the stria terminalis from the amygdala . The nuclei habenulares on both sides are connected to one another via the commissura habenularum .
The area pretectalis , also called pretectum , borders on the midbrain and contains several different core areas, the nuclei pretectales . In detail, usually seven nuclei are delineated on each side , all of which receive direct afferents from the retina , in some cases also from photosensitive ganglion cells . Efferents emanate from the pretectal nucleus in particular and contribute to the reflective narrowing of the pupil when exposed to light. Since some of these efferents cross over the posterior commissure to the other side (to the Edinger-Westphal nucleus on the opposite side), both pupils always narrow simultaneously (so-called consensual response ) during the pupillary light reflex .
The commissura posterior epithalamica is a cross connection not only for efferents of pretectal nuclei, but primarily the mutual superior colliculi (in animals: colliculi rostrales ) in the lamina tecti - the roof of the midbrain ( tectum mesencephali ; in birds: tectum opticum ) - and for the optical coordination of reflective eye movements is essential.
The subcommissural organ lies under the commissura posterior in the roof of the III. Ventricle . Its ependymal cells secrete u. a. a filamentous glycoprotein ( Reissner's thread ) into the inner liquor space, which may play a role in the embryonic development of chordates .