Survivorship bias
Survivorship bias (German: survival error ) refers to a cognitive bias . After the survivorship bias, the probabilities of success are systematically overestimated because successful people or conditions are more visible than unsuccessful ones.
history
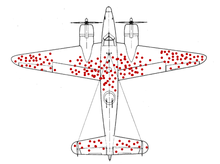
The term goes back to the work of Allied engineers in World War II , who wanted to improve the armor of the aircraft and thus increase the survival rate of the pilots. They first reinforced the armor of the returned machines in the places with the most bullet holes. However, this did not improve the survival rate. The mathematician Abraham Wald finally recognized the error and suggested armoring the aircraft more where there were no bullet holes, since hits at these points obviously triggered a crash and thus made it impossible to return.
Examples
economy
Fund companies liquidate unsuccessful funds after a certain period of time. As a result, the collective performance of the group of actively managed funds as a whole is shown better than is actually justified, since the “bankrupt” funds are constantly falling off the balance sheet.
In customer satisfaction surveys , individuals who still have a positive attitude towards the company are much more likely to respond than those who have a negative opinion. Sometimes the goal of recognizing and improving the problematic aspects of the customer relationship is missed. This is known as the bogus silence in surveys .
For business start -Seminars successful business people are invited as speakers rather as unsuccessful as company founders and their experiences are ignored. This leads to the erroneous assumption that a successful company formation is the norm.
medicine
In medicine, survivorship bias plays a prominent role. For example, cancer patients who do not respond to established treatment methods sometimes take part in experimental therapy. The problem now is that the patient remains ill, but has to survive long enough for the new type of therapy to be considered at all. Thus, it cannot be clearly established what benefit the experimental therapy would show in the early stages of the disease.
architecture
The fact that high-quality or aesthetically high-quality buildings are in operation for longer and are less likely to be demolished leads to the "finding" that in earlier epochs seemingly better architectural achievements were performed. The fact that the homes of wealthy citizens are made of more durable materials gives the impression that things were built more solidly in earlier times: another distortion.
Popular culture
As with examples from business, it is not clear to the observer that for every prominent actor or singer there are thousands of artists who never managed to become famous. In children and young people, this contributes to the belief that it is easy to become a “star”.
Antidote
Since the survivorship bias corresponds, so to speak, to a retrospective case-control study without a control group, a prospective study must be carried out. In the example of the combat aircraft, all aircraft that took off for action should be taken into account in the sample. In customer surveys, for example, all customers who placed their first order in a certain period of time can be interviewed - instead of just asking current customers for their opinion. In the same way, one can examine the success of entrepreneurs by drawing up a list of start-ups from the commercial register instead of looking at the companies currently in existence.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Wirtz, M. (2020). Failure of survival. In MA Wirtz (ed.), Dorsch - Lexicon of Psychology . Retrieved on April 13, 2020, from portal.hogrefe.com/dorsch/ueberlebensirrtum
- ↑ a b Hanno Beck: It depends on the loser . October 6, 2012. Retrieved March 15, 2015.
- ^ Elton, Gruber, Blake: Survivorship Bias and Mutual Fund Performance . In: Review of Financial Studies . 9, No. 4, 1996, pp. 1097-1120. doi : 10.1093 / rfs / 9.4.1097 .