Blackboard equation
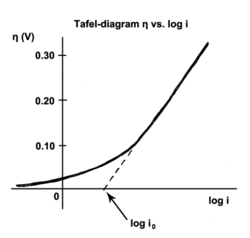
In the field of electrochemistry, the Tafel equation approximately describes the relationship between the current density at an electrode and the electrode potential . It is named after Julius Tafel , who found it empirically in 1905 . The Tafel equation is useful for calculating the cell voltage of electrochemical cells, especially for electrolysis. It is also important for the discussion of the voltage drop in a fuel cell at a given current, here one statement of the equation reads:
- For a given current, the electrochemically induced voltage drop is lower, the higher the exchange current of the cell.
The exchange current depends on the catalyst used in the fuel cell . It is therefore a goal of the further development of fuel cells to find catalysts that maximize this current.
Formula of the Tafel equation
The Tafel equation only applies approximately in a medium current range. The more precise Butler-Volmer equation must be used for smaller currents or small overvoltages .
Here are:
: the voltage drop : the general gas constant : the absolute temperature : the penetration or symmetry factor : the number of electrons transferred : the Faraday constant : the exchange current density: the current density
Individual evidence
- ↑ Julius Tafel: About the polarization during cathodic hydrogen evolution. In: Wilhelm Ostwald, JH van't Hoff (Hrsg.): Journal for physical chemistry, stoichiometry and kinship theory . tape 50 . Wilhelm Engelmann, Leipzig 1905, p. 641-712 , doi : 10.1515 / zpch-1905-5043 ( PDF ).