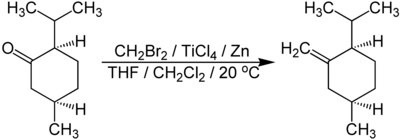
Takai-Lombardo reaction
The Takai-Lombardo reaction in organic chemistry is a reaction for the methylenation (as well as olefination) of unreactive ketones . It is related to Takai methylenation (named after the Japanese chemist Kazuhiko Takai ) and was inspired by this reaction. The Lombardo reagent is used , a methylenation reagent that was published by Luciano Lombardo .
Lombardo reagent and Takai-Lombardo methylenation
The Lombardo reagent is made in situ from titanium (IV) chloride , elemental zinc and dibromomethane in THF . It is a mild, non-basic methylenation of ketones ( aldehydes react under the same conditions to form the pinacol product ). Ketones are not enolized under the reaction conditions, i.e. α-chiral centers are retained and are not epimerized. Numerous functional groups are compatible with the reagent and the reaction conditions such as THP ethers , TBDMS ethers , acetals , esters , carboxylic acids , alcohols and lactones .
Takai-Lombardy olefination
In contrast to methylenation , alkylidation ( olefination ; not to be confused with Takai olefination ) could not be reliably reproduced at first. Many zinc sources contained traces of lead, which explains the initially poor reproducibility. By adding catalytic amounts of lead (Pb powder or PbCl 2 ), it is possible to reliably transfer sterically demanding alkylidene groups. The reaction is therefore not limited to dibromomethane (CH 2 Br 2 ) and can be extended to terminal dibromides (RCHBr 2 ), which makes the Takai-Lombardo reaction an alternative for other olefinations (e.g. Wittig, Peterson, Julia) . The originally poor reproducibility of the alkylidation with RCHBr 2 has meant that the Takai-Lombardo reaction is often represented in abbreviated form as methylenation with dibromomethane. To avoid misunderstandings, the Takai-Lombardo methylenation with dibromomethane can better be viewed as a popular special case of the Takai-Lombardo reaction. Even if one regards the olefination as an extension of the actual reaction with the Lobardo reagent, Lombardo methylenation and olefination can be more clearly differentiated from one another and combined together to form the Takai-Lombardo reaction. The related chromium-based Takai reactions (methylenation by the Takai reaction and its extension, the Takai-Utimoto olefination) are comparable. Here, too, a sharper linguistic delimitation could prove useful.
mechanism
The reaction mechanism of the reaction is unknown. However, there is suspicion that the reaction occurs via a bimetalated species.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Luciano Lombardo: Methylenation of Carbonyl Compounds: (+) - 3-METHYLENE-cis-p-METHANE In: Organic Syntheses . 65, 1987, p. 81, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.065.0081 ; Coll. Vol. 8, 1993, pp. 386-392 ( PDF ).
- ↑ L. Lombardo: Methylenation of carbonyl compounds with Zn --- CH 2 Br 2 --- TiCl 4 . Application to gibberellins in Tetrahedron Lett. 23 (1982) 4293-4296. doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4039 (00) 88728-6 .
- ↑ Kazuhiko Takai, Tadahiro Kakiuchi, Yasutaka Kataoka, Kiitiro Utimoto: A Novel Catalytic Effect of Lead on the Reduction of a Zinc Carbenoid with Zinc Metal Leading to a Geminal Dizinc Compound. Acceleration of the Wittig-Type Olefination with the RCHX2-TiCl4-Zn Systems by Addition of Lead . In: The Journal of Organic Chemistry . tape 59 , no. May 10 , 1994, ISSN 0022-3263 , pp. 2668-2670 , doi : 10.1021 / jo00089a002 .