Tesla as
| Tesla as | |
|---|---|
| legal form | as |
| founding | January 18, 1921 |
| Seat | Prague , Czech Republic |
| Website | www.tesla.cz |
Tesla (in relation to Nikola Tesla , also as the backronym Te chnika sla boproudá, German for "low voltage technology") was a large state-owned association of electronics manufacturers in Czechoslovakia from 1946 .
What is left of this today is a trademark and name components of existing companies in Slovakia and the Czech Republic .
history
The company was founded on January 18, 1921 as Elektra . Between 1932 and 1945 it belonged to Philips . After the Second World War, it became a state-owned group of electronics companies, which since March 7, 1946, under the name TESLA, primarily supplied the Eastern Bloc in the areas of radio and radar technology . Non-socialist export countries were, for example, Syria and Egypt.
The passive radar division was spun off in 1994 as ERA as .
In 2007 TESLA was awarded to an Irish investor and in 2012 it was bought back by the Czech management.
In a dispute with the US electric car manufacturer Tesla, Inc. , rights of use were granted to the brand in 2010.
Products
In addition to systems and large devices, TESLA's product range also included electronic components, loudspeakers, telephones and consumer electronics ( entertainment electronics ) such as radios, tape recorders and televisions.
In 1945 the production of light bulbs, electron tubes and radios began. Tesla light bulbs found their way to Austria and Germany as promotional items from 1980/2000.
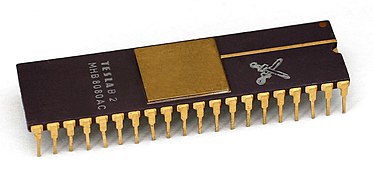
From the beginning of the 1980s, the construction of various integrated circuits began , such as the MHB8080A , a clone of the 8080 microprocessor from Intel , which is built into the MAŤO home computer manufactured between 1989 and 1992 , and the MH3212 , a replica of the Intel-I / O chip 8212 , which was used in the IQ 151 for example.
In the German-speaking area, TESLA products were known almost exclusively in the GDR , as they were often not competitive on the world market. In the Comecon area , however, TESLA had a monopoly on some products.
TESLA also produced air traffic control radars on a larger scale , mostly initially as a license production of a Soviet predecessor with subsequent in-house development. These radar devices were used in the entire RGW and are partly still in operation due to their robust mechanics and have only been subject to extensive modernization with a switch from tube to semiconductor technology. This part of the production was divided into several small companies, which are still on the market in this business area.
Tesla also produced the passive radars KOPÁČ, Ramona and Tamara for military purposes.
Electronic components from TESLA: (2 power transistors in the TO-3 housing and electron tube )
MAŤO , home computer 1989–1992
literature
- Michael Philipp Strassmann: TESLA - the history of a state-owned company and its entertainment electronics devices. Funkverlag Hein, Dessau 2007, ISBN 978-3-936124-21-7 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ P. Chadraba: The Central and Eastern European markets. Haworth Press, 1995, ISBN 1-56024-712-6 , 111 pages, page 5
- ↑ About us - TESLA Stropkov. tesla.sk, accessed on August 24, 2015 .
- ↑ TESLA history. History in facts (TESLA in the Czech Republic). tesla.cz, accessed on August 24, 2015 (English).
- ↑ a b ERA as: Company history
- ^ Till Janzer: Electronics company Tesla back in Czech hands. radio.cz/de, July 31, 2012, accessed on August 24, 2015 .
- ↑ Tesla Resolves nagging trademark dispute. marketwatch.com, December 2, 2010, accessed August 24, 2015 .
- ^ Gert Redlich: The Eastern Europeans - TESLA-ČSSR. (No longer available online.) Dlt.magnetbandmuseum.info, formerly in the original ; accessed on August 24, 2015 . ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Tesla b4 at www.ddr-museum.de
- ↑ Historical radar device from TESLA, presented in the radar tutorial: RP-3F