Tosylates
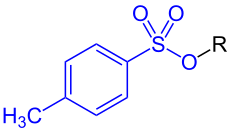
| Tosylate ( three oxygen atoms) |
|
p -Toluolsulfonsäureester (tosylate) to the blue labeled tosylate group bound to an organic radical R. The tosylate group containing 3 oxygen atoms. |
|
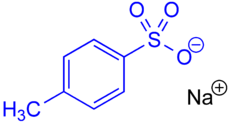
Sodium salt of p -toluenesulfonic acid with the blue- marked tosylate anion ( tosylate group ). The tosylate anion contains 3 oxygen atoms. |
Tosylates are esters or salts of p -toluenesulfonic acid .
INN nomenclature
In the medical and pharmaceutical sector, the internationally recognized short form for the anion of p-toluenesulfonic acid (p-toluenesulfonate) is "tosilate" according to the INN rules. Such short forms are created for molecular components if their systematic designation is too long. The “modified INN” (INNm) is created by combining a short form with the INN of the active component of the drug. Examples of such modified INN are for example ittramine tosilate or suplatast tosilate , the actual active ingredients are the bases of the counterions.
Likelihood of confusion
| Tosyl group ( two oxygen atoms) |
|
The tosyl group marked blue contains only 2 oxygen atoms. In the formula, R stands, for example, for Cl (tosyl chloride), NH 2 , NH-alkyl or N (alkyl) 2 (tosylamides), OH ( p -toluenesulfonic |
The tosylate group always contains three oxygen atoms that are directly bonded to the sulfur atom. The tosylate group should not be confused with the tosyl group ; according to IUPAC rule C-641.7, the latter only contains two oxygen atoms bound to an organyl oxy residue (OR) or, for example, a chlorine atom in tosyl chloride .
Manufacturing
Tosylates can be produced by deprotonating an alcohol and then reacting with p -toluenesulphonic acid chloride, whereby one equivalent of hydrogen chloride , which is bound as a hydrochloride by a base , is formed:
use
Due to their property as a leaving group, tosylates are used in preparative organic chemistry . By converting alcohols into tosylates, the poor leaving group HO - is converted into a good leaving group, which enables substitution reactions at this position on the carbon structure. The anion of p -toluenesulfonic acid emerges as a leaving group . Even more reactive than the esters of p -toluenesulfonic acid (tosylates) are the corresponding triflates , which react up to 10,000 times faster and in which the 4-methylphenyl residue of the tosylate is replaced by a trifluoromethyl residue (hence the name triflate).
Drugs that an amino group be included sometimes as salts of p used toluenesulfonic acid, so as tosylates.
Individual evidence
- ↑ International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for pharmaceutical substances - Names for radicals, groups & others , WHO 2012.
- ↑ a b Author collective, Organikum , 21st edition, p. 217, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2001, ISBN 3-527-29985-8 .