Wadi el-Melek
|
Wadi el-Melek Wadi el-Malik; Wadi al-Milk |
||
|
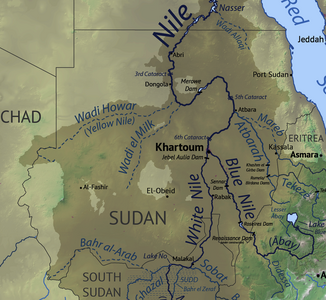
The catchment area of the Nile in Sudan with the Wadi Melek (center) |
||
| Data | ||
| location |
|
|
| River system | Nile | |
| Drain over | Nile → Mediterranean | |
| source | Northwest of en-Nahud 13 ° 46 ′ 0 ″ N , 27 ° 53 ′ 0 ″ E |
|
| Source height | approx. 650 m | |
| muzzle | at ad-Dabba (Debba) coordinates: 18 ° 3 ′ 0 ″ N , 30 ° 57 ′ 0 ″ E 18 ° 3 ′ 0 ″ N , 30 ° 57 ′ 0 ″ E
|
|
| length | approx. 500 km | |
| Dried out along its entire length | ||
The Wadi el-Melek is a wadi in Sudan .
geography
The Wadi el-Melek rises northwest of en-Nahud in the Kordofan region , first flows north, then bends northeast at around 16 ° 10 'N 28 ° 48' E, runs south along the Gebel al-Ain and joins it ad-Dabba in the Nile.
The upper reaches of the wadi system and its surroundings are characterized by steppe or dry steppe vegetation. The Wadital in the area of the bend to the northeast is particularly fertile. Here the wadi serves as a grazing area for numerous semi-nomadic groups, e.g. B. the Kababish .
archeology
Numerous archaeological sites testify to a long settlement of the wadi since the Iron Age . B. the settlement of Zankor on its upper course, several medieval sites in the area of Gebel al-Ain , as well as the fortified well station Kufriyat al-Attash on its lower course, which cannot yet be precisely dated .
literature
- Sudan Survey Office, Khartoum. Topographic maps 44, 45, 54. 1927–52