Wide mouthed gloss snail
| Wide mouthed gloss snail | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Wide-mouthed gloss snail ( Aegopinella nitens ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Aegopinella nitens | ||||||||||||
| ( Michaud , 1831) |
The wide- mouthed gloss snail ( Aegopinella nitens ) is a species of land-living snail belonging to the family of the gloss snail (Oxychilidae). The species is also found in Germany.
features
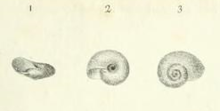
The right -hand wound housing is low-conical with 4 to 4½ turns. It is 8 to 11 mm wide and 4 to 5.5 mm high. A housing width of 14 mm can be achieved in the Alps. The turns are moderately arched and increase regularly. The last quarter of the end turn is more or less widened towards the mouth, and sometimes also more or less beveled. However, it usually does not decrease, or does not decrease significantly. The mouth is oblique-elliptical in plan and about three times as wide as the penultimate turn. It is inclined to the coil axis. The mouth edge is straight and sharp. The navel is clearly eccentric.
The housing is greenish brown to light horn brown and translucent. The base around the navel is milky-whitish. The growing stripes with weaker spiral lines form a weak grid pattern, which can only be seen clearly when the case is fresh.
The soft body is bluish to dark blue. The sides towards the sole become lighter, the sole is milky white. The upper tentacles are black-blue. In the male genital tract, the penis is large and wide. It is divided into two sections by a constriction a little below the middle. The upper end tapers almost abruptly and merges into the epiphallus. The point of attachment of the penile retractor muscle is just before the transition. In the female part, the free fallopian tube is comparatively long, the vagina is thickened and short. The stem of the spermathek is very short, the bladder barely reaches the egg ladder (spermoviduct).
Similar species
The shell of the wide-mouthed gloss snail is very similar to that of the misunderstood gloss snail ( Aegopinella epipedostoma ). Most of the time, the mouth is not widened as much and does not sink as much. In individual cases, however, only an examination of the genital system can provide final certainty. The misunderstood gloss snail has a club-shaped swelling in the upper part of the vagina, into which the short stalk of the spermathek joins. The epiphallus and penis are shorter than those of the misunderstood gloss snail ( Aegopinella epipedostoma ), the strong constriction of the penis is missing. The penile retractor muscle attaches roughly in the middle of the epiphallus. The shell of the reddish gloss snail ( Aegopinella nitidula ) is usually somewhat smaller. In this type, the penis is not so swollen, it also lacks the strong constriction. The transition between epiphallus and penis is more gradual, not as abrupt as in the large-mouthed gloss snail.
Geographical distribution and habitat
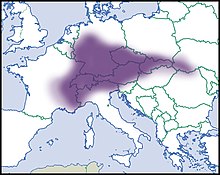
The distribution area extends from the Western Alps to the Eastern and Southern Alps to the Czech Republic, Slovakia, southern Poland and western Ukraine. In the north it extends as far as the German low mountain ranges Harz and Teutoburg Forest; individual occurrences are also known from Belgium and the Netherlands.
The long-mouthed gloss snail prefers to live under the leaf litter and under stones in forests or between rocks, in moderately moist locations on chalky soils in the mountains. Occasionally, it is also found in arid locations with loose soils. It seldom rises above 1,500 m above sea level, but occasionally up to 2,500 m.
Way of life
Between June and August, and much later in warmer areas, 30 to 50 eggs are laid in clusters of 6 to 9 eggs under the leaves of the leaf litter. The eggs have a diameter of 1.0 to 1.6 mm. The young hatch after about two weeks. Sexual maturity is only reached in the second year.
The animals feed on withered parts of the plant, but they also hunt smaller species of snails.
Taxonomy
The taxon was proposed by André Louis Gaspard Michaud in 1831 as Helix nitens Michaud, 1831. It is now generally accepted as belonging to the genus Aegopinella Lindholm, 1927.
Danger
The species is considered endangered in Lower Saxony. Viewed across Germany, however, it is not endangered. The IUCN also classifies them as not at risk.
literature
- Klaus Bogon: Land snails biology, ecology, biotope protection. 404 p., Natur Verlag, Augsburg 1990, ISBN 3-89440-002-1 , p. 196/97.
- Michael P. Kerney, RAD Cameron, Jürgen H. Jungbluth: The land snails of Northern and Central Europe. 384 pp., Paul Parey, Hamburg & Berlin 1983, ISBN 3-490-17918-8 , pp. 114/15
- Adolf Riedel: About the Aegopinella species (Gastropoda, Zonitidae) from Yugoslavia, Italy and France. Annales Zoologici, 37 (5): 235-258, 1983 PDF
Individual evidence
- ^ A b André Louis Gaspard Michaud: Complément de l'histoire naturelle des mollusques terrestres et fluviatiles de la France, de JPR Draparnaud. SI-XV (= 1-15), 1-116, Lippmann, Verdun, 1831 Online at Biodiversity Heritage Library , p. 44 plate 15 Fig. 1-5
- ↑ Jürgen H. Jungbluth and Dietrich von Knorre: Trivial names of land and freshwater mollusks in Germany (Gastropoda et Bivalvia). Mollusca, 26 (1): 105-156, Dresden 2008 ISSN 1864-5127 , p. 123.
- ↑ a b c Francisco W. Welter Schultes: European non-marine molluscs, a guide for species identification = identification book for European land and freshwater mollusks. A1-A3 S., 679 S., Q1-Q78 S., Göttingen, Planet Poster Ed., 2012 ISBN 3-933922-75-5 , ISBN 978-3-933922-75-5 (p. 397)
- ↑ Species summary for Chondrina avenacea . In: Animal Base. Uni Göttingen, June 25, 2009, accessed June 8, 2010 .
- ↑ Fauna Europaea: Aegopinella nitens (Michaud, 1831)
- ↑ MolluscaBase: Aegopinella nitens (Michaud, 1831)
- ↑ a b Vollrath Wiese: The land snails of Germany. 352 pp., Quelle & Meyer, Wiebelsheim 2014 ISBN 978-3-494-01551-4 (p. 176)
- ↑ The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Aegopinella nitens (Michaud, 1831)